文件系统过滤驱动
过滤
分层驱动中再加一层而不影响上下层,以过滤他们之间的数据,对数据进行安全控制。
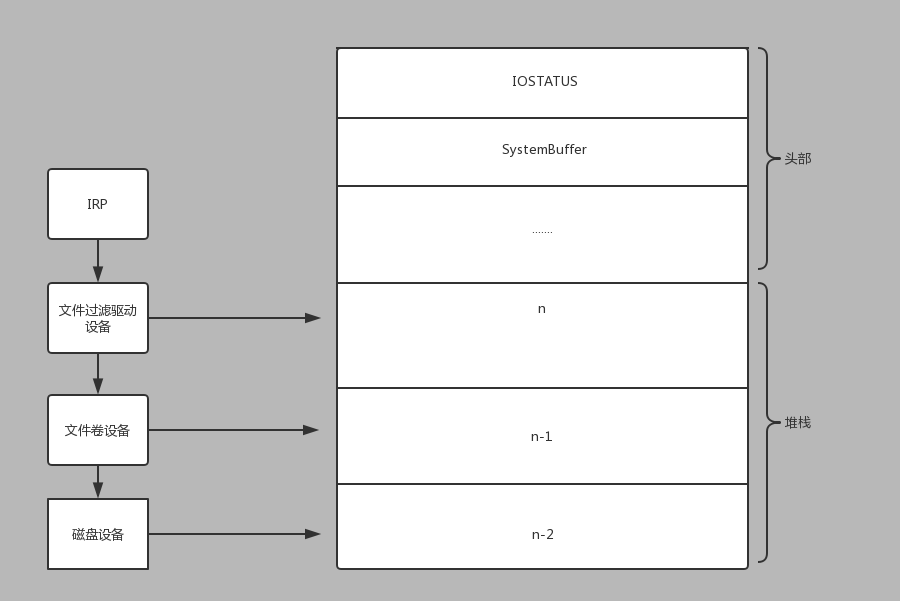
IRP分头部和栈,应用层的命令和数据通过I/O管理器封装在IRP中然后逐层发给下层驱动创建的设备对象进行处理。
Sfilter诞生于很早之前。快要被淘汰,但是了解Sfilter对于整个文件驱动框架的理解很是关键。
绑定
控制设备
DriverEntry中创建,生成的设备对象专门和用户自己的客户端进行通讯
过滤设备
生成的设备对象绑定到其他设备之上,接受其他R3
驱动自己生成一个设备,调用系统提供的API,绑定到目标设备上,并返回一个在未绑定之前目标设备所在设备栈的最顶层设备。
绑定API:
IoAttachDevice()
IoAttachDeviceToDeviceStackSafe()
IoAttachDeviceToDeviceStack()
返回未绑定之前目标设备所在设备栈的最顶层设备是用于IRP下发,并将返回的设备对象保存在目标设备的设备扩展里面。
设备对象结构体DEVICE_OBJECT
Sfilter代码
typedef struct DECLSPEC_ALIGN(MEMORY_ALLOCATION_ALIGNMENT) _DEVICE_OBJECT
{
CSHORT Type;
USHORT Size;
LONG ReferenceCount;
/*指向驱动程序中驱动对象的指针*/
struct _DRIVER_OBJECT *DriverObject;
/*指向下一个设备对象的指针*/
struct _DEVICE_OBJECT *NextDevice;
/*上一个设备对象的指针*/
struct _DEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedDevice;
/*当前IRP结构*/
struct _IRP *CurrentIrp;
PIO_TIMER Timer;
/*设备对象的特性标志*/
ULONG Flags;
ULONG Characteristics;
_volatile PVPB Vpb;
/*指向设备扩展对象的指针*/
PVOID DeviceExtension;
/*指明设备类型*/
DEVICE_TYPE DeviceType;
/*堆栈的最小层数*/
CCHAR StackSize;
union {
LIST_ENTRY ListEntry;
WAIT_CONTEXT_BLOCK Wcb;
} Queue;
/*内存对齐*/
ULONG AlignmentRequirement;
KDEVICE_QUEUE DeviceQueue;
KDPC Dpc;
/*
*下列成员用于支持文件系统的互斥操作
*以便对文件系统处理线程使用设备的计数保持跟踪
*/
ULONG ActiveThreadCount;
PSECURITY_DESCRIPTOR SecurityDescriptor;
KEVENT DeviceLock;
USHORT SectorSize;
USHORT Spare1;
struct _DEVOBJ_EXTENSION *DeviceObjectExtension;
PVOID Reserved;
} DEVICE_OBJECT;
typedef struct _DEVICE_OBJECT *PDEVICE_OBJECT;
如何区分自己进程和别的进程的IRP?
区分是控制设备还是过滤设备,控制设备指针保存。过滤设备是否自己生成,扩展设备是否为空。
/*++
Copyright (c) 1989-2004 Microsoft Corporation
Module Name:
sfilter.c
Abstract:
This module contains the code that implements the general purpose sample
file system filter driver.
As of the Windows XP SP1 IFS Kit version of this sample and later, this
sample can be built for each build environment released with the IFS Kit
with no additional modifications. To provide this capability, additional
compile-time logic was added -- see the '#if WINVER' locations. Comments
tagged with the 'VERSION NOTE' header have also been added as appropriate to
describe how the logic must change between versions.
If this sample is built in the Windows XP environment or later, it will run
on Windows 2000 or later. This is done by dynamically loading the routines
that are only available on Windows XP or later and making run-time decisions
to determine what code to execute. Comments tagged with 'MULTIVERISON NOTE'
mark the locations where such logic has been added.
Environment:
Kernel mode
--*/
//
// Fixes Win2K compatibility regarding lookaside lists.
//
#ifndef _WIN2K_COMPAT_SLIST_USAGE
#define _WIN2K_COMPAT_SLIST_USAGE
#endif
#include "precomp.h"
//
// Enable these warnings in the code.
//
#pragma warning(error:4100) // Unreferenced formal parameter
#pragma warning(error:4101) // Unreferenced local variable
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Macro and Structure Definitions
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// The following useful macros are defined in NTIFS.H in Windows XP and later.
// We will define them locally if we are building for the Windows 2000
// environment.
//
#if WINVER == 0x0500
//
// These macros are used to test, set and clear flags respectively
//
#ifndef FlagOn
#define FlagOn(_F,_SF) ((_F) & (_SF))
#endif
#ifndef BooleanFlagOn
#define BooleanFlagOn(F,SF) ((BOOLEAN)(((F) & (SF)) != 0))
#endif
#ifndef SetFlag
#define SetFlag(_F,_SF) ((_F) |= (_SF))
#endif
#ifndef ClearFlag
#define ClearFlag(_F,_SF) ((_F) &= ~(_SF))
#endif
#define RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString(_ucStr,_buf,_bufSize) \
((_ucStr)->Buffer = (_buf), \
(_ucStr)->Length = 0, \
(_ucStr)->MaximumLength = (USHORT)(_bufSize))
#ifndef min
#define min(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#endif
#ifndef max
#define max(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#endif
//
// We want ASSERT defined as an expression, which was fixed after Windows 2000
//
#ifdef ASSERT
#undef ASSERT
#if DBG
#define ASSERT( exp ) \
((!(exp)) ? \
(RtlAssert( #exp, __FILE__, __LINE__, NULL ),FALSE) : \
TRUE)
#else
#define ASSERT( exp ) ((void) 0)
#endif
#endif
#define ExFreePoolWithTag( a, b ) ExFreePool( (a) )
#endif /* WINVER == 0x0500 */
#ifndef Add2Ptr
#define Add2Ptr(P,I) ((PVOID)((PUCHAR)(P) + (I)))
#endif
//
// Buffer size for local names on the stack
//
#define MAX_DEVNAME_LENGTH 64
#define CONSTANT_UNICODE_STRING(s) { sizeof( s ) - sizeof( WCHAR ), sizeof(s), s }
//
// Device extension definition for our driver. Note that the same extension
// is used for the following types of device objects:
// - File system device object we attach to
// - Mounted volume device objects we attach to
//
typedef struct _SFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION {
//
// NL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER contains all the fields that are needed by
// the name lookup library. It happens to contain all fields SFilter needs
// for its device extension.
//
NL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader;
//
// Local flags for this device
//
ULONG Flags;
} SFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION, *PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION;
//
// If set, disable all special debug options on this volume
//
#define SFDEVFL_DISABLE_VOLUME 0x00000001
//
// This structure contains the information we need to pass to the completion
// processing for FSCTRLs.
//
typedef struct _FSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT {
//
// The workitem that will be initialized with our context and
// worker routine if this completion processing needs to be completed
// in a worker thread.
//
WORK_QUEUE_ITEM WorkItem;
//
// The device object to which this device is currently directed.
//
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject;
//
// The IRP for this FSCTRL operation.
//
PIRP Irp;
//
// For mount operations, the new device object that we have allocated
// and partially initialized that we will attach to the mounted volume
// if the mount is successful.
//
PDEVICE_OBJECT NewDeviceObject;
} FSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT, *PFSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT;
//
// Macro to test if this is my device object
//
#define IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT(_devObj) \
(((_devObj) != NULL) && \
((_devObj)->DriverObject == gSFilterDriverObject) && \
((_devObj)->DeviceExtension != NULL))
//
// Macro to test if this is my control device object
//
#define IS_MY_CONTROL_DEVICE_OBJECT(_devObj) \
(((_devObj) == gSFilterControlDeviceObject) ? \
(ASSERT(((_devObj)->DriverObject == gSFilterDriverObject) && \
((_devObj)->DeviceExtension == NULL)), TRUE) : \
FALSE)
//
// Macro to test for device types we want to attach to
//
#define IS_DESIRED_DEVICE_TYPE(_type) \
(((_type) == FILE_DEVICE_DISK_FILE_SYSTEM) || \
((_type) == FILE_DEVICE_CD_ROM_FILE_SYSTEM) || \
((_type) == FILE_DEVICE_NETWORK_FILE_SYSTEM))
//
// Macro to test if FAST_IO_DISPATCH handling routine is valid
//
#define VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER(_FastIoDispatchPtr, _FieldName) \
(((_FastIoDispatchPtr) != NULL) && \
(((_FastIoDispatchPtr)->SizeOfFastIoDispatch) >= \
(FIELD_OFFSET(FAST_IO_DISPATCH, _FieldName) + sizeof(void *))) && \
((_FastIoDispatchPtr)->_FieldName != NULL))
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
//
// MULTIVERSION NOTE:
//
// If built in the Windows XP environment or later, we will dynamically import
// the function pointers for routines that were not supported on Windows 2000
// so that we can build a driver that will run, with modified logic, on
// Windows 2000 or later.
//
// Below are the prototypes for the function pointers that we need to
// dynamically import because not all OS versions support these routines.
//
typedef
NTSTATUS
(*PSF_REGISTER_FILE_SYSTEM_FILTER_CALLBACKS) (
IN PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject,
IN PFS_FILTER_CALLBACKS Callbacks
);
typedef
NTSTATUS
(*PSF_ENUMERATE_DEVICE_OBJECT_LIST) (
IN PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT *DeviceObjectList,
IN ULONG DeviceObjectListSize,
OUT PULONG ActualNumberDeviceObjects
);
typedef
NTSTATUS
(*PSF_ATTACH_DEVICE_TO_DEVICE_STACK_SAFE) (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT SourceDevice,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT TargetDevice,
OUT PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedToDeviceObject
);
typedef
PDEVICE_OBJECT
(*PSF_GET_LOWER_DEVICE_OBJECT) (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
typedef
PDEVICE_OBJECT
(*PSF_GET_DEVICE_ATTACHMENT_BASE_REF) (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
typedef
NTSTATUS
(*PSF_GET_DISK_DEVICE_OBJECT) (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT FileSystemDeviceObject,
OUT PDEVICE_OBJECT *DiskDeviceObject
);
typedef
PDEVICE_OBJECT
(*PSF_GET_ATTACHED_DEVICE_REFERENCE) (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
typedef
NTSTATUS
(*PSF_GET_VERSION) (
IN OUT PRTL_OSVERSIONINFOW VersionInformation
);
typedef struct _SF_DYNAMIC_FUNCTION_POINTERS {
//
// The following routines should all be available on Windows XP (5.1) and
// later.
//
PSF_REGISTER_FILE_SYSTEM_FILTER_CALLBACKS RegisterFileSystemFilterCallbacks;
PSF_ATTACH_DEVICE_TO_DEVICE_STACK_SAFE AttachDeviceToDeviceStackSafe;
PSF_ENUMERATE_DEVICE_OBJECT_LIST EnumerateDeviceObjectList;
PSF_GET_LOWER_DEVICE_OBJECT GetLowerDeviceObject;
PSF_GET_DEVICE_ATTACHMENT_BASE_REF GetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef;
PSF_GET_DISK_DEVICE_OBJECT GetDiskDeviceObject;
PSF_GET_ATTACHED_DEVICE_REFERENCE GetAttachedDeviceReference;
PSF_GET_VERSION GetVersion;
} SF_DYNAMIC_FUNCTION_POINTERS, *PSF_DYNAMIC_FUNCTION_POINTERS;
SF_DYNAMIC_FUNCTION_POINTERS gSfDynamicFunctions = {0};
//
// MULTIVERSION NOTE: For this version of the driver, we need to know the
// current OS version while we are running to make decisions regarding what
// logic to use when the logic cannot be the same for all platforms. We
// will look up the OS version in DriverEntry and store the values
// in these global variables.
//
ULONG gSfOsMajorVersion = 0;
ULONG gSfOsMinorVersion = 0;
//
// Here is what the major and minor versions should be for the various
// OS versions:
//
// OS Name MajorVersion MinorVersion
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Windows 2000 5 0
// Windows XP 5 1
// Windows Server 2003 5 2
//
#define IS_WINDOWS2000() \
((gSfOsMajorVersion == 5) && (gSfOsMinorVersion == 0))
#define IS_WINDOWSXP() \
((gSfOsMajorVersion == 5) && (gSfOsMinorVersion == 1))
#define IS_WINDOWSXP_OR_LATER() \
(((gSfOsMajorVersion == 5) && (gSfOsMinorVersion >= 1)) || \
(gSfOsMajorVersion > 5))
#define IS_WINDOWSSRV2003_OR_LATER() \
(((gSfOsMajorVersion == 5) && (gSfOsMinorVersion >= 2)) || \
(gSfOsMajorVersion > 5))
#endif
//
// Tags identifying memory SFilter allocates
//
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_FASTIO 'ifFS'
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_MOUNTVOL 'vmFS'
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_LOADFS 'flFS'
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_ENUMFSVOL 'neFS'
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_DOSNAME 'ndFS'
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_NAME_BUFFER 'bnFS'
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_BIGNAMEBUFFER 'nbFS'
#define SFLT_POOL_TAG_DEVNAME 'nvFS'
//
// Macros for SFilter DbgPrint levels.
//
// #define SF_LOG_PRINT( _dbgLevel, _string ) \
// (FlagOn(SfDebug,(_dbgLevel)) ? \
// DbgPrint _string : \
// ((void)0))
#define SF_LOG_PRINT( _dbgLevel, _string ) \
(FlagOn(SfDebug,(_dbgLevel)) ? \
DbgPrint _string : \
DbgPrint _string)
//
// Delay values for KeDelayExecutionThread()
// (Values are negative to represent relative time)
//
#define DELAY_ONE_MICROSECOND (-10)
#define DELAY_ONE_MILLISECOND (DELAY_ONE_MICROSECOND*1000)
#define DELAY_ONE_SECOND (DELAY_ONE_MILLISECOND*1000)
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Global variables
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Lookaside list for various name buffers.
//
PAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST gSfNameBufferLookasideList;
//
// Since we always use this list to allocate NAME_CONTROLs, we will use that
// for the size of the lookaside list.
//
#define SFILTER_LOOKASIDE_SIZE sizeof( NAME_CONTROL )
//
// Holds pointer to the driver object for this driver
//
PDRIVER_OBJECT gSFilterDriverObject = NULL;
//
// Holds pointer to the device object that represents this driver and is used
// by external programs to access this driver. This is also known as the
// "control device object".
//
PDEVICE_OBJECT gSFilterControlDeviceObject = NULL;
//
// This lock is used to synchronize our attaching to a given device object.
// This lock fixes a race condition where we could accidently attach to the
// same device object more then once. This race condition only occurs if
// a volume is being mounted at the same time as this filter is being loaded.
// This problem will never occur if this filter is loaded at boot time before
// any file systems are loaded.
//
// This lock is used to atomically test if we are already attached to a given
// device object and if not, do the attach.
//
FAST_MUTEX gSfilterAttachLock;
UNICODE_STRING gInsufficientResourcesUnicode = CONSTANT_UNICODE_STRING(L"[-= Insufficient Resources =-]");
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Debug Definitions
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Display names of device objects we attach to.
//
#define SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES 0x00000001
//
// Get file names (during create) and display them (create completion).
//
#define SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CREATE_NAMES 0x00000002
//
// Get file names but don't display them (during create).
//
#define SFDEBUG_GET_CREATE_NAMES 0x00000004
//
// Do create completion routine, regardless of name display.
//
#define SFDEBUG_DO_CREATE_COMPLETION 0x00000008
//
// Do attach to FSRecognizer device objects.
//
#define SFDEBUG_ATTACH_TO_FSRECOGNIZER 0x00000010
//
// Do attach to ShadowCopy Volume device objects -- they are only around on
// Windows XP and later.
//
#define SFDEBUG_ATTACH_TO_SHADOW_COPIES 0x00000020
//
// Do get and use DOS device names for file name display.
//
#define SFDEBUG_GET_DOS_NAMES 0x00000040
//
// Display information at cleanup/close time
//
#define SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CLEANUPCLOSE_NAMES 0x00000080
//
// Global which holds debug state
//
ULONG SfDebug = SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CREATE_NAMES;
//
// Given a device type, return a valid name.
//
#define GET_DEVICE_TYPE_NAME( _type ) \
((((_type) > 0) && \
((_type) < (sizeof(DeviceTypeNames) / sizeof(PCHAR)))) ? \
DeviceTypeNames[ (_type) ] : \
"[Unknown]")
//
// Known device type names.
//
static const PCHAR DeviceTypeNames[] = {
"",
"BEEP",
"CD_ROM",
"CD_ROM_FILE_SYSTEM",
"CONTROLLER",
"DATALINK",
"DFS",
"DISK",
"DISK_FILE_SYSTEM",
"FILE_SYSTEM",
"INPORT_PORT",
"KEYBOARD",
"MAILSLOT",
"MIDI_IN",
"MIDI_OUT",
"MOUSE",
"MULTI_UNC_PROVIDER",
"NAMED_PIPE",
"NETWORK",
"NETWORK_BROWSER",
"NETWORK_FILE_SYSTEM",
"NULL",
"PARALLEL_PORT",
"PHYSICAL_NETCARD",
"PRINTER",
"SCANNER",
"SERIAL_MOUSE_PORT",
"SERIAL_PORT",
"SCREEN",
"SOUND",
"STREAMS",
"TAPE",
"TAPE_FILE_SYSTEM",
"TRANSPORT",
"UNKNOWN",
"VIDEO",
"VIRTUAL_DISK",
"WAVE_IN",
"WAVE_OUT",
"8042_PORT",
"NETWORK_REDIRECTOR",
"BATTERY",
"BUS_EXTENDER",
"MODEM",
"VDM",
"MASS_STORAGE",
"SMB",
"KS",
"CHANGER",
"SMARTCARD",
"ACPI",
"DVD",
"FULLSCREEN_VIDEO",
"DFS_FILE_SYSTEM",
"DFS_VOLUME",
"SERENUM",
"TERMSRV",
"KSEC"
};
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Function Prototypes
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Define driver entry routine.
//
NTSTATUS
DriverEntry(
IN PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject,
IN PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath
);
#if DBG && WINVER >= 0x0501
VOID
DriverUnload(
IN PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject
);
#endif
//
// Define the local routines used by this driver module. This includes a
// a sample of how to filter a create file operation, and then invoke an I/O
// completion routine when the file has successfully been created/opened.
//
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
VOID
SfLoadDynamicFunctions (
VOID
);
VOID
SfGetCurrentVersion (
VOID
);
#endif
NTSTATUS
SfPassThrough (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
);
NTSTATUS
SfCreate (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
);
NTSTATUS
SfCreateCompletion (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp,
IN PVOID Context
);
NTSTATUS
SfCleanupClose (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
);
NTSTATUS
SfFsControl (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
);
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlMountVolume (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
);
VOID
SfFsControlMountVolumeCompleteWorker (
IN PFSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT Context
);
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlMountVolumeComplete (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT NewDeviceObject
);
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlLoadFileSystem (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
);
VOID
SfFsControlLoadFileSystemCompleteWorker (
IN PFSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT Context
);
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlLoadFileSystemComplete (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
);
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlCompletion (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp,
IN PVOID Context
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoCheckIfPossible (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN ULONG LockKey,
IN BOOLEAN CheckForReadOperation,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoRead (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PVOID Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoWrite (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN ULONG LockKey,
IN PVOID Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryBasicInfo (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
OUT PFILE_BASIC_INFORMATION Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryStandardInfo (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
OUT PFILE_STANDARD_INFORMATION Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoLock (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER Length,
PEPROCESS ProcessId,
ULONG Key,
BOOLEAN FailImmediately,
BOOLEAN ExclusiveLock,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoUnlockSingle (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER Length,
PEPROCESS ProcessId,
ULONG Key,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoUnlockAll (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
PEPROCESS ProcessId,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoUnlockAllByKey (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
PVOID ProcessId,
ULONG Key,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoDeviceControl (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN PVOID InputBuffer OPTIONAL,
IN ULONG InputBufferLength,
OUT PVOID OutputBuffer OPTIONAL,
IN ULONG OutputBufferLength,
IN ULONG IoControlCode,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
VOID
SfFastIoDetachDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT SourceDevice,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT TargetDevice
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryNetworkOpenInfo (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
OUT PFILE_NETWORK_OPEN_INFORMATION Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlRead (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlReadComplete (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoPrepareMdlWrite (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlWriteComplete (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoReadCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PVOID Buffer,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
OUT struct _COMPRESSED_DATA_INFO *CompressedDataInfo,
IN ULONG CompressedDataInfoLength,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoWriteCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
IN PVOID Buffer,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN struct _COMPRESSED_DATA_INFO *CompressedDataInfo,
IN ULONG CompressedDataInfoLength,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlReadCompleteCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlWriteCompleteCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryOpen (
IN PIRP Irp,
OUT PFILE_NETWORK_OPEN_INFORMATION NetworkInformation,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
#if WINVER >= 0x0501 /* See comment in DriverEntry */
NTSTATUS
SfPreFsFilterPassThrough (
IN PFS_FILTER_CALLBACK_DATA Data,
OUT PVOID *CompletionContext
);
VOID
SfPostFsFilterPassThrough (
IN PFS_FILTER_CALLBACK_DATA Data,
IN NTSTATUS OperationStatus,
IN PVOID CompletionContext
);
#endif
VOID
SfFsNotification (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN BOOLEAN FsActive
);
NTSTATUS
SfAttachDeviceToDeviceStack (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT SourceDevice,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT TargetDevice,
IN OUT PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedToDeviceObject
);
NTSTATUS
SfAttachToFileSystemDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PNAME_CONTROL DeviceName
);
VOID
SfDetachFromFileSystemDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
NTSTATUS
SfAttachToMountedDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT SFilterDeviceObject
);
VOID
SfCleanupMountedDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
);
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
NTSTATUS
SfEnumerateFileSystemVolumes (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT FSDeviceObject
);
#endif
NTSTATUS
SfGetBaseDeviceObjectName (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN OUT PNAME_CONTROL DeviceName
);
BOOLEAN
SfIsAttachedToDevice (
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedDeviceObject OPTIONAL
);
BOOLEAN
SfIsAttachedToDeviceW2K (
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedDeviceObject OPTIONAL
);
BOOLEAN
SfIsAttachedToDeviceWXPAndLater (
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedDeviceObject OPTIONAL
);
VOID
SfReadDriverParameters (
IN PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath
);
NTSTATUS
SfIsShadowCopyVolume (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT StorageStackDeviceObject,
OUT PBOOLEAN IsShadowCopy
);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Assign text sections for each routine.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifdef ALLOC_PRAGMA
#pragma alloc_text(INIT, DriverEntry)
#if DBG && WINVER >= 0x0501
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, DriverUnload)
#endif
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFsNotification)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfCreate)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfCleanupClose)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFsControl)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFsControlMountVolume)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFsControlMountVolumeComplete)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFsControlLoadFileSystem)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFsControlLoadFileSystemComplete)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoCheckIfPossible)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoRead)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoWrite)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoQueryBasicInfo)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoQueryStandardInfo)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoLock)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoUnlockSingle)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoUnlockAll)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoUnlockAllByKey)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoDeviceControl)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoDetachDevice)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoQueryNetworkOpenInfo)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoMdlRead)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoPrepareMdlWrite)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoMdlWriteComplete)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoReadCompressed)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoWriteCompressed)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfFastIoQueryOpen)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfAttachDeviceToDeviceStack)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfAttachToFileSystemDevice)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfDetachFromFileSystemDevice)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfAttachToMountedDevice)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfIsAttachedToDevice)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfIsAttachedToDeviceW2K)
#pragma alloc_text(INIT, SfReadDriverParameters)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfIsShadowCopyVolume)
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
#pragma alloc_text(INIT, SfLoadDynamicFunctions)
#pragma alloc_text(INIT, SfGetCurrentVersion)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfEnumerateFileSystemVolumes)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfIsAttachedToDeviceWXPAndLater)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, SfGetBaseDeviceObjectName)
#endif
#endif
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Functions
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
DriverEntry (
IN PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject,
IN PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This is the initialization routine for the SFILTER file system filter
driver. This routine creates the device object that represents this
driver in the system and registers it for watching all file systems that
register or unregister themselves as active file systems.
Arguments:
DriverObject - Pointer to driver object created by the system.
Return Value:
The function value is the final status from the initialization operation.
--*/
{
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
UNICODE_STRING nameString;
UNICODE_STRING dosName;
NTSTATUS status;
ULONG i;
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
//
// Try to load the dynamic functions that may be available for our use.
//
SfLoadDynamicFunctions();
//
// Now get the current OS version that we will use to determine what logic
// paths to take when this driver is built to run on various OS version.
//
SfGetCurrentVersion();
#endif
//
// Get Registry values
//
SfReadDriverParameters( RegistryPath );
//
// Save our Driver Object, set our UNLOAD routine
//
gSFilterDriverObject = DriverObject;
#if DBG && WINVER >= 0x0501
//
// MULTIVERSION NOTE:
//
// We can only support unload for testing environments if we can enumerate
// the outstanding device objects that our driver has.
//
//
// Unload is useful for development purposes. It is not recommended for
// production versions
//
if (NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList) {
gSFilterDriverObject->DriverUnload = DriverUnload;
}
#endif
//
// Setup other global variables
//
ExInitializeFastMutex( &gSfilterAttachLock );
//
// Initialize the lookaside list for name buffering. This is used in
// several places to avoid having a large name buffer on the stack. It is
// also needed by the name lookup routines (NLxxx).
//
ExInitializePagedLookasideList( &gSfNameBufferLookasideList,
NULL,
NULL,
0,
SFILTER_LOOKASIDE_SIZE,
SFLT_POOL_TAG_NAME_BUFFER,
0 );
//
// Create the Control Device Object (CDO). This object represents this
// driver. Note that it does not have a device extension.
//
RtlInitUnicodeString( &nameString, L"\\FileSystem\\Filters\\SFilterDrv" );
status = IoCreateDevice( DriverObject,
0, //has no device extension
&nameString,
FILE_DEVICE_DISK_FILE_SYSTEM,
FILE_DEVICE_SECURE_OPEN,
FALSE,
&gSFilterControlDeviceObject );
if (status == STATUS_OBJECT_PATH_NOT_FOUND) {
//
// This must be a version of the OS that doesn't have the Filters
// path in its namespace. This was added in Windows XP.
//
// We will try just putting our control device object in the
// \FileSystem portion of the object name space.
//
RtlInitUnicodeString( &nameString, L"\\FileSystem\\SFilterDrv" );
status = IoCreateDevice( DriverObject,
0, //has no device extension
&nameString,
FILE_DEVICE_DISK_FILE_SYSTEM,
FILE_DEVICE_SECURE_OPEN,
FALSE,
&gSFilterControlDeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
KdPrint( ("SFilter!DriverEntry: Error creating control device object \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
&nameString,
status ));
return status;
}
} else if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
KdPrint(( "SFilter!DriverEntry: Error creating control device object \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
&nameString, status ));
return status;
}
RtlInitUnicodeString(&dosName, L"\\DosDevices\\SFilterDrv");
status = IoCreateSymbolicLink(&dosName, &nameString);
if (NT_SUCCESS(status) == FALSE)
{
IoDeleteDevice(gSFilterControlDeviceObject);
ExDeletePagedLookasideList(&gSfNameBufferLookasideList);
return STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
}
gSFilterControlDeviceObject->Flags |= DO_BUFFERED_IO;
//
// Initialize the driver object with this device driver's entry points.
//
for (i = 0; i <= IRP_MJ_MAXIMUM_FUNCTION; i++) {
DriverObject->MajorFunction[i] = SfPassThrough;
}
//
// We will use SfCreate for all the create operations
//
DriverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_CREATE] = SfCreate;
//DriverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_CREATE_NAMED_PIPE] = SfCreate;
//DriverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_CREATE_MAILSLOT] = SfCreate;
DriverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_FILE_SYSTEM_CONTROL] = SfFsControl;//移动(U盘)卷设备绑定
DriverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_CLEANUP] = SfCleanupClose;
DriverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_CLOSE] = SfCleanupClose;
//
// Allocate fast I/O data structure and fill it in.
//
// NOTE: The following FastIo Routines are not supported:
// AcquireFileForNtCreateSection
// ReleaseFileForNtCreateSection
// AcquireForModWrite
// ReleaseForModWrite
// AcquireForCcFlush
// ReleaseForCcFlush
//
// For historical reasons these FastIO's have never been sent to filters
// by the NT I/O system. Instead, they are sent directly to the base
// file system. On Windows XP and later OS releases, you can use the new
// system routine "FsRtlRegisterFileSystemFilterCallbacks" if you need to
// intercept these callbacks (see below).
//
fastIoDispatch = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( NonPagedPool,
sizeof( FAST_IO_DISPATCH ),
SFLT_POOL_TAG_FASTIO );
if (!fastIoDispatch) {
IoDeleteDevice( gSFilterControlDeviceObject );
return STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
RtlZeroMemory( fastIoDispatch, sizeof( FAST_IO_DISPATCH ) );
fastIoDispatch->SizeOfFastIoDispatch = sizeof( FAST_IO_DISPATCH );
fastIoDispatch->FastIoCheckIfPossible = SfFastIoCheckIfPossible;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoRead = SfFastIoRead;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoWrite = SfFastIoWrite;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryBasicInfo = SfFastIoQueryBasicInfo;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryStandardInfo = SfFastIoQueryStandardInfo;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoLock = SfFastIoLock;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoUnlockSingle = SfFastIoUnlockSingle;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoUnlockAll = SfFastIoUnlockAll;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoUnlockAllByKey = SfFastIoUnlockAllByKey;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoDeviceControl = SfFastIoDeviceControl;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoDetachDevice = SfFastIoDetachDevice;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryNetworkOpenInfo = SfFastIoQueryNetworkOpenInfo;
fastIoDispatch->MdlRead = SfFastIoMdlRead;
fastIoDispatch->MdlReadComplete = SfFastIoMdlReadComplete;
fastIoDispatch->PrepareMdlWrite = SfFastIoPrepareMdlWrite;
fastIoDispatch->MdlWriteComplete = SfFastIoMdlWriteComplete;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoReadCompressed = SfFastIoReadCompressed;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoWriteCompressed = SfFastIoWriteCompressed;
fastIoDispatch->MdlReadCompleteCompressed = SfFastIoMdlReadCompleteCompressed;
fastIoDispatch->MdlWriteCompleteCompressed = SfFastIoMdlWriteCompleteCompressed;
fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryOpen = SfFastIoQueryOpen;
DriverObject->FastIoDispatch = fastIoDispatch;
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// There are 6 FastIO routines for which file system filters are bypassed as
// the requests are passed directly to the base file system. These 6 routines
// are AcquireFileForNtCreateSection, ReleaseFileForNtCreateSection,
// AcquireForModWrite, ReleaseForModWrite, AcquireForCcFlush, and
// ReleaseForCcFlush.
//
// In Windows XP and later, the FsFilter callbacks were introduced to allow
// filters to safely hook these operations. See the IFS Kit documentation for
// more details on how these new interfaces work.
//
// MULTIVERSION NOTE:
//
// If built for Windows XP or later, this driver is built to run on
// multiple versions. When this is the case, we will test
// for the presence of FsFilter callbacks registration API. If we have it,
// then we will register for those callbacks, otherwise, we will not.
//
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
{
FS_FILTER_CALLBACKS fsFilterCallbacks;
if (NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.RegisterFileSystemFilterCallbacks) {
//
// Setup the callbacks for the operations we receive through
// the FsFilter interface.
//
// NOTE: You only need to register for those routines you really
// need to handle. SFilter is registering for all routines
// simply to give an example of how it is done.
//
fsFilterCallbacks.SizeOfFsFilterCallbacks = sizeof( FS_FILTER_CALLBACKS );
fsFilterCallbacks.PreAcquireForSectionSynchronization = SfPreFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PostAcquireForSectionSynchronization = SfPostFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PreReleaseForSectionSynchronization = SfPreFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PostReleaseForSectionSynchronization = SfPostFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PreAcquireForCcFlush = SfPreFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PostAcquireForCcFlush = SfPostFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PreReleaseForCcFlush = SfPreFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PostReleaseForCcFlush = SfPostFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PreAcquireForModifiedPageWriter = SfPreFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PostAcquireForModifiedPageWriter = SfPostFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PreReleaseForModifiedPageWriter = SfPreFsFilterPassThrough;
fsFilterCallbacks.PostReleaseForModifiedPageWriter = SfPostFsFilterPassThrough;
status = (gSfDynamicFunctions.RegisterFileSystemFilterCallbacks)( DriverObject,
&fsFilterCallbacks );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
DriverObject->FastIoDispatch = NULL;
ExFreePoolWithTag( fastIoDispatch, SFLT_POOL_TAG_FASTIO );
IoDeleteDevice( gSFilterControlDeviceObject );
return status;
}
}
}
#endif
//
// The registered callback routine "SfFsNotification" will be called
// whenever a new file systems is loaded or when any file system is
// unloaded.
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// On Windows XP and later this will also enumerate all existing file
// systems (except the RAW file systems). On Windows 2000 this does not
// enumerate the file systems that were loaded before this filter was
// loaded.
//
status = IoRegisterFsRegistrationChange( DriverObject, SfFsNotification );//文件系统设备绑定,是卷设备绑定的前提
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
KdPrint(( "SFilter!DriverEntry: Error registering FS change notification, status=%08x\n",
status ));
DriverObject->FastIoDispatch = NULL;
ExFreePoolWithTag( fastIoDispatch, SFLT_POOL_TAG_FASTIO );
IoDeleteDevice( gSFilterControlDeviceObject );
return status;
}
//
// Attempt to attach to the appropriate RAW file system device objects
// since they are not enumerated by IoRegisterFsRegistrationChange.
//
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT rawDeviceObject;
PFILE_OBJECT fileObject;
//
// Attach to RawDisk device
//
RtlInitUnicodeString( &nameString, L"\\Device\\RawDisk" );
status = IoGetDeviceObjectPointer(
&nameString,
FILE_READ_ATTRIBUTES,
&fileObject,
&rawDeviceObject );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
SfFsNotification( rawDeviceObject, TRUE );
ObDereferenceObject( fileObject );
}
//
// Attach to the RawCdRom device
//
RtlInitUnicodeString( &nameString, L"\\Device\\RawCdRom" );
status = IoGetDeviceObjectPointer(
&nameString,
FILE_READ_ATTRIBUTES,
&fileObject,
&rawDeviceObject );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
SfFsNotification( rawDeviceObject, TRUE );
ObDereferenceObject( fileObject );
}
}
//
// Clear the initializing flag on the control device object since we
// have now successfully initialized everything.
//
ClearFlag( gSFilterControlDeviceObject->Flags, DO_DEVICE_INITIALIZING );
DbgPrint("Sfilter installed\n");
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
#if DBG && WINVER >= 0x0501
VOID
DriverUnload (
IN PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is called when a driver can be unloaded. This performs all of
the necessary cleanup for unloading the driver from memory. Note that an
error can NOT be returned from this routine.
When a request is made to unload a driver the IO System will cache that
information and not actually call this routine until the following states
have occurred:
- All device objects which belong to this filter are at the top of their
respective attachment chains.
- All handle counts for all device objects which belong to this filter have
gone to zero.
WARNING: Microsoft does not officially support the unloading of File
System Filter Drivers. This is an example of how to unload
your driver if you would like to use it during development.
This should not be made available in production code.
Arguments:
DriverObject - Driver object for this module
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
NTSTATUS status;
ULONG numDevices;
ULONG i;
LARGE_INTEGER interval;
UNICODE_STRING ustrLinkName;
# define DEVOBJ_LIST_SIZE 64
PDEVICE_OBJECT devList[DEVOBJ_LIST_SIZE];
ASSERT(DriverObject == gSFilterDriverObject);
//
// Log we are unloading.
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!DriverUnload: Unloading driver (%p)\n",
DriverObject) );
//
// Don't get anymore file system change notifications.
//
IoUnregisterFsRegistrationChange( DriverObject, SfFsNotification );
//
// Free the name buffer lookaside list.
//
ExDeletePagedLookasideList( &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
//
// This is the loop that will go through all of the devices we are attached
// to and detach from them. Since we don't know how many there are and
// we don't want to allocate memory (because we can't return an error)
// we will free them in chunks using a local array on the stack.
//
for (;;) {
//
// Get what device objects we can for this driver. Quit if there
// are not any more. Note that this routine should always be
// defined since this routine is only compiled for Windows XP and
// later.
//
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList );
status = (gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList)(
DriverObject,
devList,
sizeof(devList),
&numDevices);
if (numDevices <= 0) {
break;
}
numDevices = min( numDevices, DEVOBJ_LIST_SIZE );
//
// First go through the list and detach each of the devices.
// Our control device object does not have a DeviceExtension and
// is not attached to anything so don't detach it.
//
for (i=0; i < numDevices; i++) {
devExt = devList[i]->DeviceExtension;
if (NULL != devExt) {
IoDetachDevice( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject );
}
}
//
// The IO Manager does not currently add a reference count to a device
// object for each outstanding IRP. This means there is no way to
// know if there are any outstanding IRPs on the given device.
// We are going to wait for a reasonable amount of time for pending
// IRPs to complete.
//
// WARNING: This does not work 100% of the time and the driver may be
// unloaded before all IRPs are completed. This can easily
// occur under stress situations and if a long lived IRP is
// pending (like opLocks and directory change notifications).
// The system will fault when this IRP actually completes.
// This is a sample of how to do this during testing. This
// is not recommended for production code.
//
interval.QuadPart = (5 * DELAY_ONE_SECOND); //delay 5 seconds
KeDelayExecutionThread( KernelMode, FALSE, &interval );
//
// Now go back through the list and delete the device objects.
//
for (i=0; i < numDevices; i++) {
//
// See if this is our control device object. If not then cleanup
// the device extension. If so then clear the global pointer
// that references it.
//
if (NULL != devList[i]->DeviceExtension) {
SfCleanupMountedDevice( devList[i] );
} else {
ASSERT(devList[i] == gSFilterControlDeviceObject);
gSFilterControlDeviceObject = NULL;
}
//
// Delete the device object, remove reference counts added by
// IoEnumerateDeviceObjectList. Note that the delete does
// not actually occur until the reference count goes to zero.
//
IoDeleteDevice( devList[i] );
ObDereferenceObject( devList[i] );
}
}
//
// Free our FastIO table
//
RtlInitUnicodeString(&ustrLinkName, L"\\DosDevices\\SFilterDrv");
IoDeleteSymbolicLink(&ustrLinkName);
fastIoDispatch = DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
DriverObject->FastIoDispatch = NULL;
ExFreePoolWithTag( fastIoDispatch, SFLT_POOL_TAG_FASTIO );
}
#endif
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
VOID
SfLoadDynamicFunctions (
VOID
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine tries to load the function pointers for the routines that
are not supported on all versions of the OS. These function pointers are
then stored in the global structure SpyDynamicFunctions.
This support allows for one driver to be built that will run on all
versions of the OS Windows 2000 and greater. Note that on Windows 2000,
the functionality may be limited.
Arguments:
None.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
UNICODE_STRING functionName;
RtlZeroMemory( &gSfDynamicFunctions, sizeof( gSfDynamicFunctions ) );
//
// For each routine that we would want to use, lookup its address in the
// kernel or HAL. If it is not present, that field in our global
// SpyDynamicFunctions structure will be set to NULL.
//
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"FsRtlRegisterFileSystemFilterCallbacks" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.RegisterFileSystemFilterCallbacks = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"IoAttachDeviceToDeviceStackSafe" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.AttachDeviceToDeviceStackSafe = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"IoEnumerateDeviceObjectList" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"IoGetLowerDeviceObject" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.GetLowerDeviceObject = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"IoGetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"IoGetDiskDeviceObject" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDiskDeviceObject = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"IoGetAttachedDeviceReference" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.GetAttachedDeviceReference = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
RtlInitUnicodeString( &functionName, L"RtlGetVersion" );
gSfDynamicFunctions.GetVersion = MmGetSystemRoutineAddress( &functionName );
}
VOID
SfGetCurrentVersion (
VOID
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine reads the current OS version using the correct routine based
on what routine is available.
Arguments:
None.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
if (NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetVersion) {
RTL_OSVERSIONINFOW versionInfo;
NTSTATUS status;
//
// VERSION NOTE: RtlGetVersion does a bit more than we need, but
// we are using it if it is available to show how to use it. It
// is available on Windows XP and later. RtlGetVersion and
// RtlVerifyVersionInfo (both documented in the IFS Kit docs) allow
// you to make correct choices when you need to change logic based
// on the current OS executing your code.
//
versionInfo.dwOSVersionInfoSize = sizeof( RTL_OSVERSIONINFOW );
status = (gSfDynamicFunctions.GetVersion)( &versionInfo );
ASSERT( NT_SUCCESS( status ) );
gSfOsMajorVersion = versionInfo.dwMajorVersion;
gSfOsMinorVersion = versionInfo.dwMinorVersion;
} else {
PsGetVersion( &gSfOsMajorVersion,
&gSfOsMinorVersion,
NULL,
NULL );
}
}
#endif
VOID
SfFsNotification (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN BOOLEAN FsActive
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is invoked whenever a file system has either registered or
unregistered itself as an active file system.
For the former case, this routine creates a device object and attaches it
to the specified file system's device object. This allows this driver
to filter all requests to that file system. Specifically we are looking
for MOUNT requests so we can attach to newly mounted volumes.
For the latter case, this file system's device object is located,
detached, and deleted. This removes this file system as a filter for
the specified file system.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the file system's device object.
FsActive - Boolean indicating whether the file system has registered
(TRUE) or unregistered (FALSE) itself as an active file system.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
PNAME_CONTROL devName;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Display the names of all the file system we are notified of
//
devName = NLGetAndAllocateObjectName( DeviceObject,
&gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
if (devName == NULL) {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsNotification: Not attaching to %p, insufficient resources.\n",
DeviceObject) );
return;
}
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsNotification: %s %p \"%wZ\" (%s)\n",
(FsActive) ? "Activating file system " : "Deactivating file system",
DeviceObject,
&devName->Name,
GET_DEVICE_TYPE_NAME(DeviceObject->DeviceType)) );
//
// Handle attaching/detaching from the given file system.
//
if (FsActive) {
SfAttachToFileSystemDevice( DeviceObject, devName );
} else {
SfDetachFromFileSystemDevice( DeviceObject );
}
//
// We're done with name (SfAttachToFileSystemDevice copies the name to
// the device extension) so free it.
//
NLFreeNameControl( devName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// IRP Handling Routines
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
SfPassThrough (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the main dispatch routine for the general purpose file
system driver. It simply passes requests onto the next driver in the
stack, which is presumably a disk file system.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the device object for this driver.
IRP - Pointer to the request packet representing the I/O request.
Return Value:
The function value is the status of the operation.
Note:
A note to file system filter implementers:
This routine actually "passes" through the request by taking this
driver out of the IRP stack. If the driver would like to pass the
I/O request through, but then also see the result, then rather than
taking itself out of the loop it could keep itself in by copying the
caller's parameters to the next stack location and then set its own
completion routine.
Hence, instead of calling:
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
You could instead call:
IoCopyCurrentIrpStackLocationToNext( Irp );
IoSetCompletionRoutine( Irp, NULL, NULL, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE );
This example actually NULLs out the caller's I/O completion routine, but
this driver could set its own completion routine so that it would be
notified when the request was completed (see SfCreate for an example of
this).
--*/
{
PIO_STACK_LOCATION pIrp = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
//
// Sfilter doesn't allow handles to its control device object to be
// created, therefore, no other operation should be able to come through.
//
ASSERT(!IS_MY_CONTROL_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// File systems should NEVER receive a power IRP
//
ASSERT(pIrp->MajorFunction != IRP_MJ_POWER);
//
// Get this driver out of the driver stack and get to the next driver as
// quickly as possible.
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
//
// Call the appropriate file system driver with the request.
//
return IoCallDriver( ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
Irp );
}
NTSTATUS
SfCreate (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This function filters create/open operations. It simply establishes an
I/O completion routine to be invoked if the operation was successful.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the target device object of the create/open.
Irp - Pointer to the I/O Request Packet that represents the operation.
Return Value:
The function value is the status of the call to the file system's entry
point.
--*/
{
NTSTATUS status;
PNAME_CONTROL fileName = NULL;
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt = (PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION)(DeviceObject->DeviceExtension);
PIO_STACK_LOCATION irpSp = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
BOOLEAN cacheName;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// If this is for our control device object, don't allow it to be opened.
//
if (IS_MY_CONTROL_DEVICE_OBJECT(DeviceObject)) {
//
// Sfilter doesn't allow for any communication through its control
// device object, therefore it fails all requests to open a handle
// to its control device object.
//
// See the FileSpy sample for an example of how to allow creates to
// the filter's control device object and manage communication via
// that handle.
//
//Irp->IoStatus.Status = STATUS_INVALID_DEVICE_REQUEST;
Irp->IoStatus.Status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
Irp->IoStatus.Information = 0;
IoCompleteRequest( Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT );
//return STATUS_INVALID_DEVICE_REQUEST;
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// If debugging is enabled, do the processing required to see the packet
// upon its completion. Otherwise, let the request go with no further
// processing.
//
if (!FlagOn( SfDebug, SFDEBUG_DO_CREATE_COMPLETION |
SFDEBUG_GET_CREATE_NAMES|
SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CREATE_NAMES )) {
//
// We don't want to get filenames, display filenames, or
// call our completion routine. Don't put us on the stack
// and call the next driver.
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
return IoCallDriver( ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
Irp );
}
if (FlagOn( SfDebug, SFDEBUG_GET_CREATE_NAMES |
SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CREATE_NAMES ) &&
!FlagOn(devExt->Flags,SFDEVFL_DISABLE_VOLUME)) {
//
// Debugging specifies that we need to get the filename
//
NAME_LOOKUP_FLAGS LookupFlags = 0x00000000;
//
// If DosName has been set, indicate via flags that we
// want to use it when getting the full file name.
//
if (devExt->NLExtHeader.DosName.Length != 0) {
SetFlag( LookupFlags, NLFL_USE_DOS_DEVICE_NAME );
}
//
// Indicate we are in pre-create
//
SetFlag( LookupFlags, NLFL_IN_CREATE );
if (FlagOn( irpSp->Parameters.Create.Options, FILE_OPEN_BY_FILE_ID )) {
//
// The file is being opened by ID, not file name.
//
SetFlag( LookupFlags, NLFL_OPEN_BY_ID );
}
if (FlagOn( irpSp->Flags, SL_OPEN_TARGET_DIRECTORY )) {
//
// The file's parent directory should be opened
//
SetFlag( LookupFlags, NLFL_OPEN_TARGET_DIR );
}
//
// Retrieve the file name. Note that in SFilter we don't do any name
// caching.
//
status = NLAllocateNameControl( &fileName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// We are okay not checking the return value here because
// the GetFullPathName function will set the Unicode String
// length to 0. So either way, in an error it will print an empty string
//
status = NLGetFullPathName( irpSp->FileObject,
fileName,
&devExt->NLExtHeader,
LookupFlags,
&gSfNameBufferLookasideList,
&cacheName );
}
}
if (FlagOn( SfDebug, SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CREATE_NAMES |
SFDEBUG_DO_CREATE_COMPLETION ) &&
!FlagOn(devExt->Flags,SFDEVFL_DISABLE_VOLUME)) {
//
// Debugging flags indicate we must do completion.
// Note that to display file names we must do completion
// because we don't know IoStatus.Status and IoStatus.Information
// until post-create.
//
KEVENT waitEvent;
//
// Initialize an event to wait for the completion routine to occur
//
KeInitializeEvent( &waitEvent, NotificationEvent, FALSE );
//
// Copy the stack and set our Completion routine
//
IoCopyCurrentIrpStackLocationToNext( Irp );
IoSetCompletionRoutine(
Irp,
SfCreateCompletion,
&waitEvent,
TRUE,
TRUE,
TRUE );
//
// Call the next driver in the stack.
//
status = IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
//
// Wait for the completion routine to be called
//
if (STATUS_PENDING == status) {
NTSTATUS localStatus = KeWaitForSingleObject( &waitEvent,
Executive,
KernelMode,
FALSE,
NULL );
ASSERT(STATUS_SUCCESS == localStatus);
}
//
// Verify the IoCompleteRequest was called
//
ASSERT(KeReadStateEvent(&waitEvent) ||
!NT_SUCCESS(Irp->IoStatus.Status));
//
// If debugging indicates we should display file names, do it.
//
if (irpSp->Parameters.Create.Options & FILE_OPEN_BY_FILE_ID) {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CREATE_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfCreate: OPENED fo=%p %08x:%08x %wZ (FID)\n",
irpSp->FileObject,
Irp->IoStatus.Status,
Irp->IoStatus.Information,
&fileName->Name) );
} else {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CREATE_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfCreate: OPENED fo=%p st=%08x:%08x %wZ\n",
irpSp->FileObject,
Irp->IoStatus.Status,
Irp->IoStatus.Information,
&fileName->Name) );
}
//
// Release the name control structure if we have
//
if (fileName != NULL) {
NLFreeNameControl( fileName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
}
//
// Save the status and continue processing the IRP
//
status = Irp->IoStatus.Status;
IoCompleteRequest( Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT );
return status;
} else {
//
// Free the name control if we have one
//
if (fileName != NULL) {
NLFreeNameControl( fileName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
}
//
// Debugging flags indicate we did not want to display the file name
// or call completion routine.
// (ie SFDEBUG_GET_CREATE_NAMES && !SFDEBUG_DO_CREATE_COMPLETION)
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
return IoCallDriver( ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
Irp );
}
}
NTSTATUS
SfCreateCompletion (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp,
IN PVOID Context
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This function is the create/open completion routine for this filter
file system driver. If debugging is enabled, then this function prints
the name of the file that was successfully opened/created by the file
system as a result of the specified I/O request.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the device on which the file was created.
Irp - Pointer to the I/O Request Packet the represents the operation.
Context - This driver's context parameter - unused;
Return Value:
The function value is STATUS_SUCCESS.
--*/
{
PKEVENT event = Context;
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( DeviceObject );
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( Irp );
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
KeSetEvent(event, IO_NO_INCREMENT, FALSE);
return STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED;
}
NTSTATUS
SfCleanupClose (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is invoked whenever a cleanup or a close request is to be
processed. NOTE: This routine doesn't actually do anything, it is the same
as SfPassThrough. It is only registered as the cleanup handler to ease in
debugging (You can set a Breakpoint here instead of in the generic PassThrough.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the device object for this driver.
Irp - Pointer to the request packet representing the I/O request.
Return Value:
The function value is the status of the operation.
Note:
See notes for SfPassThrough for this routine.
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt = (PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION)(DeviceObject->DeviceExtension);
PIO_STACK_LOCATION irpSp;
PAGED_CODE();
irpSp = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
//
// Sfilter doesn't allow handles to its control device object to be
// created, therefore, no other operation should be able to come through.
//
if (IS_MY_CONTROL_DEVICE_OBJECT(DeviceObject))
{
Irp->IoStatus.Status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
Irp->IoStatus.Information = 0;
IoCompleteRequest(Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT);
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
else if (!IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT(DeviceObject))
{
Irp->IoStatus.Status = STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER;
Irp->IoStatus.Information = 0;
IoCompleteRequest(Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT);
return STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
ASSERT(!IS_MY_CONTROL_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// File systems should NEVER receive a power IRP
//
ASSERT(irpSp->MajorFunction != IRP_MJ_POWER);
//
// Display cleanup/close info if requested. Note that we don't have a
// make to display so only display the file object address.
//
if (!FlagOn(devExt->Flags,SFDEVFL_DISABLE_VOLUME)) {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_CLEANUPCLOSE_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfCleanupClose: %s fo=%p\n",
((irpSp->MajorFunction == IRP_MJ_CLEANUP) ? "CLEANUP"
: "CLOSE "),
irpSp->FileObject) );
}
//
// Get this driver out of the driver stack and get to the next driver as
// quickly as possible.
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
//
// Now call the appropriate file system driver with the request.
//
return IoCallDriver( ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
Irp );
}
NTSTATUS
SfFsControl (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is invoked whenever an I/O Request Packet (IRP) w/a major
function code of IRP_MJ_FILE_SYSTEM_CONTROL is encountered. For most
IRPs of this type, the packet is simply passed through. However, for
some requests, special processing is required.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the device object for this driver.
Irp - Pointer to the request packet representing the I/O request.
Return Value:
The function value is the status of the operation.
--*/
{
PIO_STACK_LOCATION irpSp = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Sfilter doesn't allow handles to its control device object to be
// created, therefore, no other operation should be able to come through.
//
ASSERT(!IS_MY_CONTROL_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Process the minor function code.
//
switch (irpSp->MinorFunction) {
case IRP_MN_MOUNT_VOLUME:
return SfFsControlMountVolume( DeviceObject, Irp );
case IRP_MN_LOAD_FILE_SYSTEM:
return SfFsControlLoadFileSystem( DeviceObject, Irp );
case IRP_MN_USER_FS_REQUEST:
{
switch (irpSp->Parameters.FileSystemControl.FsControlCode) {
case FSCTL_DISMOUNT_VOLUME:
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt = DeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControl: Dismounting volume %p \"%wZ\"\n",
devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName) );
break;
}
}
break;
}
}
//
// Pass all other file system control requests through.
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
return IoCallDriver( ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION)DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
Irp );
}
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlCompletion (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp,
IN PVOID Context
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is invoked for the completion of an FsControl request. It
signals an event used to re-sync back to the dispatch routine.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object that was attached to
the file system device object
Irp - Pointer to the IRP that was just completed.
Context - Pointer to the event to signal
--*/
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( DeviceObject );
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( Irp );
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
ASSERT(Context != NULL);
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
if (IS_WINDOWSXP_OR_LATER()) {
//
// On Windows XP or later, the context passed in will be an event
// to signal.
//
KeSetEvent((PKEVENT)Context, IO_NO_INCREMENT, FALSE);
} else {
#endif
//
// For Windows 2000, if we are not at passive level, we should
// queue this work to a worker thread using the workitem that is in
// Context.
//
if (KeGetCurrentIrql() > PASSIVE_LEVEL) {
//
// We are not at passive level, but we need to be to do our work,
// so queue off to the worker thread.
//
ExQueueWorkItem( (PWORK_QUEUE_ITEM) Context,
DelayedWorkQueue );
} else {
PWORK_QUEUE_ITEM workItem = Context;
//
// We are already at passive level, so we will just call our
// worker routine directly.
//
(workItem->WorkerRoutine)(workItem->Parameter);
}
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
}
#endif
return STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED;
}
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlMountVolume (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This processes a MOUNT VOLUME request.
NOTE: The device object in the MountVolume parameters points
to the top of the storage stack and should not be used.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the VDO we are attaching to.
Irp - Pointer to the request packet representing the I/O request.
Return Value:
The status of the operation.
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt = DeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
PIO_STACK_LOCATION irpSp = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
PDEVICE_OBJECT newDeviceObject;
PDEVICE_OBJECT storageStackDeviceObject;
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION newDevExt;
NTSTATUS status;
BOOLEAN isShadowCopyVolume;
PFSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT completionContext;
PNAME_CONTROL newDeviceName;
PAGED_CODE();
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
ASSERT(IS_DESIRED_DEVICE_TYPE(DeviceObject->DeviceType));
//
// Get the real device object (also known as the storage stack device
// object or the disk device object) pointed to by the VPB parameter
// because this VPB may be changed by the underlying file system.
// Both FAT and CDFS may change the VPB address if the volume being
// mounted is one they recognize from a previous mount.
//
storageStackDeviceObject = irpSp->Parameters.MountVolume.Vpb->RealDevice;
//
// Determine if this is a shadow copy volume. If so don't attach to it.
// NOTE: There is no reason sfilter shouldn't attach to these volumes,
// this is simply a sample of how to not attach if you don't want
// to
//
status = SfIsShadowCopyVolume ( storageStackDeviceObject,
&isShadowCopyVolume );
if (NT_SUCCESS(status) &&
isShadowCopyVolume &&
!FlagOn(SfDebug,SFDEBUG_ATTACH_TO_SHADOW_COPIES)) {
PNAME_CONTROL shadowDeviceName;
//
// Get the name for the debug display
//
shadowDeviceName = NLGetAndAllocateObjectName( storageStackDeviceObject,
&gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume Not attaching to Volume %p \"%wZ\", shadow copy volume\n",
storageStackDeviceObject,
shadowDeviceName ? &shadowDeviceName->Name :
&gInsufficientResourcesUnicode) );
if (shadowDeviceName != NULL) {
NLFreeNameControl( shadowDeviceName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
}
//
// Go to the next driver
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
return IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
}
//
// This is a mount request. Create a device object that can be
// attached to the file system's volume device object if this request
// is successful. We allocate this memory now since we can not return
// an error in the completion routine.
//
// Since the device object we are going to attach to has not yet been
// created (it is created by the base file system) we are going to use
// the type of the file system control device object. We are assuming
// that the file system control device object will have the same type
// as the volume device objects associated with it.
//
status = IoCreateDevice( gSFilterDriverObject,
sizeof( SFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION ),
NULL,
DeviceObject->DeviceType,
0,
FALSE,
&newDeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// If we can not attach to the volume, then don't allow the volume
// to be mounted.
//
KdPrint(( "SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume: Error creating volume device object, status=%08x\n",
status ));
Irp->IoStatus.Information = 0;
Irp->IoStatus.Status = status;
IoCompleteRequest( Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT );
return status;
}
newDevExt = newDeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
//
// Initialize the device extension.
//
newDevExt->Flags = 0;
NLInitDeviceExtensionHeader( &newDevExt->NLExtHeader,
newDeviceObject,
storageStackDeviceObject );
//
// Get the name of this device. We need to be sure and free this device
// name (and possibly other things) in the name lookup extension header
// when we tear down the device extension in SfCleanupMountedDevice.
//
# define MVInsufResMsg "SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume Not attaching to Volume %p, Insufficient Resources.\n"
newDeviceName = NLGetAndAllocateObjectName( storageStackDeviceObject,
&gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
if (newDeviceName == NULL) {
//
// Couldn't allocate space for the device name. Go to the next driver.
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
(MVInsufResMsg,
DeviceObject) );
IoDeleteDevice( newDeviceObject );
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
return IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
}
//
// Save the name in our device object extension
//
status = NLAllocateAndCopyUnicodeString( &newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
&newDeviceName->Name,
SFLT_POOL_TAG_DEVNAME );
//
// Release name control
//
NLFreeNameControl( newDeviceName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
//
// If we couldn't copy the name we are low on resources, quit now
//
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
(MVInsufResMsg,
DeviceObject) );
IoDeleteDevice( newDeviceObject );
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
return IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
}
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// On Windows 2000, we cannot simply synchronize back to the dispatch
// routine to do our post-mount processing. We need to do this work at
// passive level, so we will queue that work to a worker thread from
// the completion routine.
//
// For Windows XP and later, we can safely synchronize back to the dispatch
// routine. The code below shows both methods. Admittedly, the code
// would be simplified if you chose to only use one method or the other,
// but you should be able to easily adapt this for your needs.
//
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
if (IS_WINDOWSXP_OR_LATER()) {
KEVENT waitEvent;
KeInitializeEvent( &waitEvent,
NotificationEvent,
FALSE );
IoCopyCurrentIrpStackLocationToNext ( Irp );
IoSetCompletionRoutine( Irp,
SfFsControlCompletion,
&waitEvent, //context parameter
TRUE,
TRUE,
TRUE );
status = IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
//
// Wait for the operation to complete
//
if (STATUS_PENDING == status) {
status = KeWaitForSingleObject( &waitEvent,
Executive,
KernelMode,
FALSE,
NULL );
ASSERT( STATUS_SUCCESS == status );
}
//
// Verify the IoCompleteRequest was called
//
ASSERT(KeReadStateEvent(&waitEvent) ||
!NT_SUCCESS(Irp->IoStatus.Status));
status = SfFsControlMountVolumeComplete( DeviceObject,//完成之后创建出来的卷设备对象
Irp,
newDeviceObject );
} else {
#endif
//
// Initialize our completion routine
//
completionContext = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( NonPagedPool,
sizeof( FSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT ),
SFLT_POOL_TAG_MOUNTVOL );
if (completionContext == NULL) {
//
// If we cannot allocate our completion context, we will just pass
// through the operation. If your filter must be present for data
// access to this volume, you should consider failing the operation
// if memory cannot be allocated here.
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
status = IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
} else {
ExInitializeWorkItem( &completionContext->WorkItem,
SfFsControlMountVolumeCompleteWorker,
completionContext );
completionContext->DeviceObject = DeviceObject;
completionContext->Irp = Irp;
completionContext->NewDeviceObject = newDeviceObject;
IoCopyCurrentIrpStackLocationToNext( Irp );
IoSetCompletionRoutine( Irp,
SfFsControlCompletion,
&completionContext->WorkItem,
TRUE,
TRUE,
TRUE );
//
// Call the driver
//
status = IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
}
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
}
#endif
return status;
}
VOID
SfFsControlMountVolumeCompleteWorker (
IN PFSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT Context
)
/*++
Routine Description:
The worker thread routine that will call our common routine to do the
post-MountVolume work.
Arguments:
Context - The context passed to this worker thread.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
ASSERT( Context != NULL );
SfFsControlMountVolumeComplete( Context->DeviceObject,
Context->Irp,
Context->NewDeviceObject );
ExFreePoolWithTag( Context, SFLT_POOL_TAG_MOUNTVOL );
}
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlMountVolumeComplete (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT NewDeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This does the post-Mount work and must be done at PASSIVE_LEVEL.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The device object for this operation,
Irp - The IRP for this operation that we will complete once we are finished
with it.
Return Value:
Returns the status of the mount operation.
--*/
{
PVPB vpb;
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION newDevExt;
PIO_STACK_LOCATION irpSp;
PDEVICE_OBJECT attachedDeviceObject;
NTSTATUS status;
BOOLEAN justAttached = FALSE;
PAGED_CODE();
newDevExt = NewDeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
irpSp = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
//
// Get the correct VPB from the real device object saved in our
// device extension. We do this because the VPB in the IRP stack
// may not be the correct VPB when we get here. The underlying
// file system may change VPBs if it detects a volume it has
// mounted previously.
//
vpb = newDevExt->NLExtHeader.StorageStackDeviceObject->Vpb;
//
// Display a message when we detect that the VPB for the given
// device object has changed.
//
if (vpb != irpSp->Parameters.MountVolume.Vpb) {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume: VPB in IRP stack changed %p IRPVPB=%p VPB=%p\n",
vpb->DeviceObject,
irpSp->Parameters.MountVolume.Vpb,
vpb) );
}
//
// See if the mount was successful.
//
if (NT_SUCCESS( Irp->IoStatus.Status )) {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume: Mount volume success for %p \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
DeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
Irp->IoStatus.Status) );
//
// Acquire lock so we can atomically test if we area already attached
// and if not, then attach. This prevents a double attach race
// condition.
//
ExAcquireFastMutex( &gSfilterAttachLock );
//
// The mount succeeded. If we are not already attached, attach to the
// device object. Note: one reason we could already be attached is
// if the underlying file system revived a previous mount.
//
if (!SfIsAttachedToDevice( vpb->DeviceObject, &attachedDeviceObject )) {
//
// Attach to the new mounted volume. The file system device
// object that was just mounted is pointed to by the VPB.
//
status = SfAttachToMountedDevice( vpb->DeviceObject,
NewDeviceObject );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
justAttached = TRUE;
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume: Mount volume - attached successfully to %p \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
DeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
Irp->IoStatus.Status) );
} else {
//
// The attachment failed, cleanup. Since we are in the
// post-mount phase, we can not fail this operation.
// We simply won't be attached. The only reason this should
// ever happen at this point is if somebody already started
// dismounting the volume therefore not attaching should
// not be a problem.
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume: Mount volume - attached to volume failed %p \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
DeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
Irp->IoStatus.Status) );
SfCleanupMountedDevice( NewDeviceObject );
IoDeleteDevice( NewDeviceObject );
}
ASSERT( NULL == attachedDeviceObject );
} else {
//
// We were already attached, handle it
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume Mount volume - already attached to %p \"%wZ\"\n",
((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION)attachedDeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName) );
//
// Cleanup and delete the device object we created
//
SfCleanupMountedDevice( NewDeviceObject );
IoDeleteDevice( NewDeviceObject );
//
// Dereference the returned attached device object
//
ObDereferenceObject( attachedDeviceObject );
}
//
// Release the lock
//
ExReleaseFastMutex( &gSfilterAttachLock );
//
// If we just successfully attached to the device and the appropriate
// debug flag is set, then get the DOS device name. We couldn't
// do this above because a mutex was held.
//
if (justAttached && FlagOn( SfDebug, SFDEBUG_GET_DOS_NAMES ) &&
newDevExt->NLExtHeader.StorageStackDeviceObject != NULL) {
NLGetDosDeviceName( NewDeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader );
}
} else {
//
// The mount request failed, handle it.
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlMountVolume: Mount volume failure for %p \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
DeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
Irp->IoStatus.Status) );
//
// Cleanup and delete the device object we created
//
SfCleanupMountedDevice( NewDeviceObject );
IoDeleteDevice( NewDeviceObject );
}
//
// Complete the request.
// NOTE: We must save the status before completing because after
// completing the IRP we can not longer access it (it might be
// freed).
//
status = Irp->IoStatus.Status;
IoCompleteRequest( Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT );
return status;
}
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlLoadFileSystem (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is invoked whenever an I/O Request Packet (IRP) w/a major
function code of IRP_MJ_FILE_SYSTEM_CONTROL is encountered. For most
IRPs of this type, the packet is simply passed through. However, for
some requests, special processing is required.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - Pointer to the device object for this driver.
Irp - Pointer to the request packet representing the I/O request.
Return Value:
The function value is the status of the operation.
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt = DeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
NTSTATUS status;
PFSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT completionContext;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// This is a "load file system" request being sent to a file system
// recognizer device object. This IRP_MN code is only sent to
// file system recognizers.
//
// NOTE: Since we no longer are attaching to the standard Microsoft file
// system recognizers we will normally never execute this code.
// However, there might be 3rd party file systems which have their
// own recognizer which may still trigger this IRP.
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFscontrolLoadFileSystem: Loading File System, Detaching from \"%wZ\"\n",
&devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName) );
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// On Windows 2000, we cannot simply synchronize back to the dispatch
// routine to do our post-load filesystem processing. We need to do
// this work at passive level, so we will queue that work to a worker
// thread from the completion routine.
//
// For Windows XP and later, we can safely synchronize back to the dispatch
// routine. The code below shows both methods. Admittedly, the code
// would be simplified if you chose to only use one method or the other,
// but you should be able to easily adapt this for your needs.
//
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
if (IS_WINDOWSXP_OR_LATER()) {
KEVENT waitEvent;
KeInitializeEvent( &waitEvent,
NotificationEvent,
FALSE );
IoCopyCurrentIrpStackLocationToNext( Irp );
IoSetCompletionRoutine( Irp,
SfFsControlCompletion,
&waitEvent, //context parameter
TRUE,
TRUE,
TRUE );
//
// Detach from the file system recognizer device object.
//
IoDetachDevice( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject );
//
// Call the driver
//
status = IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
//
// Wait for the operation to complete
//
if (STATUS_PENDING == status) {
status = KeWaitForSingleObject( &waitEvent,
Executive,
KernelMode,
FALSE,
NULL );
ASSERT( STATUS_SUCCESS == status );
}
//
// Verify the IoCompleteRequest was called
//
ASSERT(KeReadStateEvent(&waitEvent) ||
!NT_SUCCESS(Irp->IoStatus.Status));
status = SfFsControlLoadFileSystemComplete( DeviceObject,
Irp );
} else {
#endif
//
// Set a completion routine so we can delete the device object when
// the load is complete.
//
completionContext = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( NonPagedPool,
sizeof( FSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT ),
SFLT_POOL_TAG_LOADFS );
if (completionContext == NULL) {
//
// If we cannot allocate our completion context, we will just pass
// through the operation. If your filter must be present for data
// access to this volume, you should consider failing the operation
// if memory cannot be allocated here.
//
IoSkipCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
status = IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
} else {
ExInitializeWorkItem( &completionContext->WorkItem,
SfFsControlLoadFileSystemCompleteWorker,
completionContext );
completionContext->DeviceObject = DeviceObject;
completionContext->Irp = Irp;
completionContext->NewDeviceObject = NULL;
IoCopyCurrentIrpStackLocationToNext( Irp );
IoSetCompletionRoutine(
Irp,
SfFsControlCompletion,
completionContext,
TRUE,
TRUE,
TRUE );
//
// Detach from the file system recognizer device object.
//
IoDetachDevice( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject );
//
// Call the driver
//
status = IoCallDriver( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject, Irp );
}
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
}
#endif
return status;
}
VOID
SfFsControlLoadFileSystemCompleteWorker (
IN PFSCTRL_COMPLETION_CONTEXT Context
)
/*++
Routine Description:
The worker thread routine that will call our common routine to do the
post-LoadFileSystem work.
Arguments:
Context - The context passed to this worker thread.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
ASSERT( NULL != Context );
SfFsControlLoadFileSystemComplete( Context->DeviceObject,
Context->Irp );
ExFreePoolWithTag( Context, SFLT_POOL_TAG_LOADFS );
}
NTSTATUS
SfFsControlLoadFileSystemComplete (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PIRP Irp
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This does the post-LoadFileSystem work and must be done as PASSIVE_LEVEL.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The device object for this operation,
Irp - The IRP for this operation that we will complete once we are finished
with it.
Return Value:
Returns the status of the load file system operation.
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt;
NTSTATUS status;
PAGED_CODE();
devExt = DeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
//
// Display the name if requested
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlLoadFileSystem: Detaching %p from recognizer \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
DeviceObject,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
Irp->IoStatus.Status) );
//
// Check status of the operation
//
if (!NT_SUCCESS( Irp->IoStatus.Status ) &&
(Irp->IoStatus.Status != STATUS_IMAGE_ALREADY_LOADED)) {
//
// The load was not successful. Simply reattach to the recognizer
// driver in case it ever figures out how to get the driver loaded
// on a subsequent call. There is not a lot we can do if this
// reattach fails.
//
SfAttachDeviceToDeviceStack( DeviceObject,
devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject );
ASSERT(devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject != NULL);
} else {
//
// The load was successful, so cleanup this device and delete the
// Device object
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFsControlLoadFileSystem: Detached %p from recognizer \"%wZ\", status=%08x\n",
DeviceObject,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
Irp->IoStatus.Status) );
SfCleanupMountedDevice( DeviceObject );
IoDeleteDevice( DeviceObject );
}
//
// Continue processing the operation
//
status = Irp->IoStatus.Status;
IoCompleteRequest( Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT );
return status;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// FastIO Handling routines
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoCheckIfPossible (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN ULONG LockKey,
IN BOOLEAN CheckForReadOperation,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for checking to see
whether fast I/O is possible for this file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be operated on.
FileOffset - Byte offset in the file for the operation.
Length - Length of the operation to be performed.
Wait - Indicates whether or not the caller is willing to wait if the
appropriate locks, etc. cannot be acquired
LockKey - Provides the caller's key for file locks.
CheckForReadOperation - Indicates whether the caller is checking for a
read (TRUE) or a write operation.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, FastIoCheckIfPossible )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoCheckIfPossible)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
Wait,
LockKey,
CheckForReadOperation,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoRead (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PVOID Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for reading from a
file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be read.
FileOffset - Byte offset in the file of the read.
Length - Length of the read operation to be performed.
Wait - Indicates whether or not the caller is willing to wait if the
appropriate locks, etc. cannot be acquired
LockKey - Provides the caller's key for file locks.
Buffer - Pointer to the caller's buffer to receive the data read.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, FastIoRead )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoRead)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
Wait,
LockKey,
Buffer,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoWrite (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN ULONG LockKey,
IN PVOID Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for writing to a
file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be written.
FileOffset - Byte offset in the file of the write operation.
Length - Length of the write operation to be performed.
Wait - Indicates whether or not the caller is willing to wait if the
appropriate locks, etc. cannot be acquired
LockKey - Provides the caller's key for file locks.
Buffer - Pointer to the caller's buffer that contains the data to be
written.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, FastIoWrite )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoWrite)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
Wait,
LockKey,
Buffer,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryBasicInfo (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
OUT PFILE_BASIC_INFORMATION Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for querying basic
information about the file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be queried.
Wait - Indicates whether or not the caller is willing to wait if the
appropriate locks, etc. cannot be acquired
Buffer - Pointer to the caller's buffer to receive the information about
the file.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, FastIoQueryBasicInfo )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryBasicInfo)(
FileObject,
Wait,
Buffer,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryStandardInfo (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
OUT PFILE_STANDARD_INFORMATION Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for querying standard
information about the file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be queried.
Wait - Indicates whether or not the caller is willing to wait if the
appropriate locks, etc. cannot be acquired
Buffer - Pointer to the caller's buffer to receive the information about
the file.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoQueryStandardInfo )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryStandardInfo)(
FileObject,
Wait,
Buffer,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoLock (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER Length,
PEPROCESS ProcessId,
ULONG Key,
BOOLEAN FailImmediately,
BOOLEAN ExclusiveLock,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for locking a byte
range within a file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be locked.
FileOffset - Starting byte offset from the base of the file to be locked.
Length - Length of the byte range to be locked.
ProcessId - ID of the process requesting the file lock.
Key - Lock key to associate with the file lock.
FailImmediately - Indicates whether or not the lock request is to fail
if it cannot be immediately be granted.
ExclusiveLock - Indicates whether the lock to be taken is exclusive (TRUE)
or shared.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, FastIoLock )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoLock)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
ProcessId,
Key,
FailImmediately,
ExclusiveLock,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoUnlockSingle (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER Length,
PEPROCESS ProcessId,
ULONG Key,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for unlocking a byte
range within a file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be unlocked.
FileOffset - Starting byte offset from the base of the file to be
unlocked.
Length - Length of the byte range to be unlocked.
ProcessId - ID of the process requesting the unlock operation.
Key - Lock key associated with the file lock.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoUnlockSingle )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoUnlockSingle)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
ProcessId,
Key,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoUnlockAll (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
PEPROCESS ProcessId,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for unlocking all
locks within a file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be unlocked.
ProcessId - ID of the process requesting the unlock operation.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
if (nextDeviceObject) {
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoUnlockAll )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoUnlockAll)(
FileObject,
ProcessId,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoUnlockAllByKey (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
PVOID ProcessId,
ULONG Key,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for unlocking all
locks within a file based on a specified key.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be unlocked.
ProcessId - ID of the process requesting the unlock operation.
Key - Lock key associated with the locks on the file to be released.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoUnlockAllByKey )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoUnlockAllByKey)(
FileObject,
ProcessId,
Key,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoDeviceControl (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
IN PVOID InputBuffer OPTIONAL,
IN ULONG InputBufferLength,
OUT PVOID OutputBuffer OPTIONAL,
IN ULONG OutputBufferLength,
IN ULONG IoControlCode,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for device I/O control
operations on a file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object representing the device to be
serviced.
Wait - Indicates whether or not the caller is willing to wait if the
appropriate locks, etc. cannot be acquired
InputBuffer - Optional pointer to a buffer to be passed into the driver.
InputBufferLength - Length of the optional InputBuffer, if one was
specified.
OutputBuffer - Optional pointer to a buffer to receive data from the
driver.
OutputBufferLength - Length of the optional OutputBuffer, if one was
specified.
IoControlCode - I/O control code indicating the operation to be performed
on the device.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the I/O status of the
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoDeviceControl )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoDeviceControl)(
FileObject,
Wait,
InputBuffer,
InputBufferLength,
OutputBuffer,
OutputBufferLength,
IoControlCode,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
VOID
SfFastIoDetachDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT SourceDevice,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT TargetDevice
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is invoked on the fast path to detach from a device that
is being deleted. This occurs when this driver has attached to a file
system volume device object, and then, for some reason, the file system
decides to delete that device (it is being dismounted, it was dismounted
at some point in the past and its last reference has just gone away, etc.)
Arguments:
SourceDevice - Pointer to my device object, which is attached
to the file system's volume device object.
TargetDevice - Pointer to the file system's volume device object.
Return Value:
None
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt;
PAGED_CODE();
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( SourceDevice ));
devExt = SourceDevice->DeviceExtension;
//
// Display name information
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfFastIoDetachDevice: Detaching %p from volume %p \"%wZ\"\n",
SourceDevice,
TargetDevice,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName) );
//
// Detach from the file system's volume device object.
//
SfCleanupMountedDevice( SourceDevice );
IoDetachDevice( TargetDevice );
IoDeleteDevice( SourceDevice );
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryNetworkOpenInfo (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN BOOLEAN Wait,
OUT PFILE_NETWORK_OPEN_INFORMATION Buffer,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for querying network
information about a file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to be queried.
Wait - Indicates whether or not the caller can handle the file system
having to wait and tie up the current thread.
Buffer - Pointer to a buffer to receive the network information about the
file.
IoStatus - Pointer to a variable to receive the final status of the query
operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoQueryNetworkOpenInfo )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryNetworkOpenInfo)(
FileObject,
Wait,
Buffer,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlRead (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for reading a file
using MDLs as buffers.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object that is to be read.
FileOffset - Supplies the offset into the file to begin the read operation.
Length - Specifies the number of bytes to be read from the file.
LockKey - The key to be used in byte range lock checks.
MdlChain - A pointer to a variable to be filled in w/a pointer to the MDL
chain built to describe the data read.
IoStatus - Variable to receive the final status of the read operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, MdlRead )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->MdlRead)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
LockKey,
MdlChain,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlReadComplete (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for completing an
MDL read operation.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, if
it has one. It should be the case that this routine is invoked only if
the MdlRead function is supported by the underlying file system, and
therefore this function will also be supported, but this is not assumed
by this driver.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to complete the MDL read upon.
MdlChain - Pointer to the MDL chain used to perform the read operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE, depending on whether or not it is
possible to invoke this function on the fast I/O path.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, MdlReadComplete )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->MdlReadComplete)(
FileObject,
MdlChain,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoPrepareMdlWrite (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for preparing for an
MDL write operation.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object that will be written.
FileOffset - Supplies the offset into the file to begin the write operation.
Length - Specifies the number of bytes to be write to the file.
LockKey - The key to be used in byte range lock checks.
MdlChain - A pointer to a variable to be filled in w/a pointer to the MDL
chain built to describe the data written.
IoStatus - Variable to receive the final status of the write operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, PrepareMdlWrite )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->PrepareMdlWrite)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
LockKey,
MdlChain,
IoStatus,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlWriteComplete (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for completing an
MDL write operation.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, if
it has one. It should be the case that this routine is invoked only if
the PrepareMdlWrite function is supported by the underlying file system,
and therefore this function will also be supported, but this is not
assumed by this driver.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to complete the MDL write upon.
FileOffset - Supplies the file offset at which the write took place.
MdlChain - Pointer to the MDL chain used to perform the write operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE, depending on whether or not it is
possible to invoke this function on the fast I/O path.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
MdlWriteComplete )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->MdlWriteComplete)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
MdlChain,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
/*******************************************************************************
UNIMPLEMENTED FAST IO ROUTINES
The following four Fast IO routines are for compression on the wire
which is not yet implemented in NT.
NOTE: It is highly recommended that you include these routines (which
do a pass-through call) so your filter will not need to be
modified in the future when this functionality is implemented in
the OS.
FastIoReadCompressed, FastIoWriteCompressed,
FastIoMdlReadCompleteCompressed, FastIoMdlWriteCompleteCompressed
*******************************************************************************/
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoReadCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
OUT PVOID Buffer,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
OUT struct _COMPRESSED_DATA_INFO *CompressedDataInfo,
IN ULONG CompressedDataInfoLength,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for reading compressed
data from a file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object that will be read.
FileOffset - Supplies the offset into the file to begin the read operation.
Length - Specifies the number of bytes to be read from the file.
LockKey - The key to be used in byte range lock checks.
Buffer - Pointer to a buffer to receive the compressed data read.
MdlChain - A pointer to a variable to be filled in w/a pointer to the MDL
chain built to describe the data read.
IoStatus - Variable to receive the final status of the read operation.
CompressedDataInfo - A buffer to receive the description of the compressed
data.
CompressedDataInfoLength - Specifies the size of the buffer described by
the CompressedDataInfo parameter.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoReadCompressed )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoReadCompressed)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
LockKey,
Buffer,
MdlChain,
IoStatus,
CompressedDataInfo,
CompressedDataInfoLength,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoWriteCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN ULONG Length,
IN ULONG LockKey,
IN PVOID Buffer,
OUT PMDL *MdlChain,
OUT PIO_STATUS_BLOCK IoStatus,
IN struct _COMPRESSED_DATA_INFO *CompressedDataInfo,
IN ULONG CompressedDataInfoLength,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for writing compressed
data to a file.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object that will be written.
FileOffset - Supplies the offset into the file to begin the write operation.
Length - Specifies the number of bytes to be write to the file.
LockKey - The key to be used in byte range lock checks.
Buffer - Pointer to the buffer containing the data to be written.
MdlChain - A pointer to a variable to be filled in w/a pointer to the MDL
chain built to describe the data written.
IoStatus - Variable to receive the final status of the write operation.
CompressedDataInfo - A buffer to containing the description of the
compressed data.
CompressedDataInfoLength - Specifies the size of the buffer described by
the CompressedDataInfo parameter.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
FastIoWriteCompressed )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->FastIoWriteCompressed)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
Length,
LockKey,
Buffer,
MdlChain,
IoStatus,
CompressedDataInfo,
CompressedDataInfoLength,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlReadCompleteCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for completing an
MDL read compressed operation.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, if
it has one. It should be the case that this routine is invoked only if
the read compressed function is supported by the underlying file system,
and therefore this function will also be supported, but this is not assumed
by this driver.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to complete the compressed read
upon.
MdlChain - Pointer to the MDL chain used to perform the read operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE, depending on whether or not it is
possible to invoke this function on the fast I/O path.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
MdlReadCompleteCompressed )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->MdlReadCompleteCompressed)(
FileObject,
MdlChain,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoMdlWriteCompleteCompressed (
IN PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
IN PLARGE_INTEGER FileOffset,
IN PMDL MdlChain,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for completing a
write compressed operation.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, if
it has one. It should be the case that this routine is invoked only if
the write compressed function is supported by the underlying file system,
and therefore this function will also be supported, but this is not assumed
by this driver.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the file object to complete the compressed write
upon.
FileOffset - Supplies the file offset at which the file write operation
began.
MdlChain - Pointer to the MDL chain used to perform the write operation.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE, depending on whether or not it is
possible to invoke this function on the fast I/O path.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch,
MdlWriteCompleteCompressed )) {
return (fastIoDispatch->MdlWriteCompleteCompressed)(
FileObject,
FileOffset,
MdlChain,
nextDeviceObject );
}
}
return FALSE;
}
BOOLEAN
SfFastIoQueryOpen (
IN PIRP Irp,
OUT PFILE_NETWORK_OPEN_INFORMATION NetworkInformation,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the fast I/O "pass through" routine for opening a file
and returning network information for it.
This function simply invokes the file system's corresponding routine, or
returns FALSE if the file system does not implement the function.
Arguments:
Irp - Pointer to a create IRP that represents this open operation. It is
to be used by the file system for common open/create code, but not
actually completed.
NetworkInformation - A buffer to receive the information required by the
network about the file being opened.
DeviceObject - Pointer to this driver's device object, the device on
which the operation is to occur.
Return Value:
The function value is TRUE or FALSE based on whether or not fast I/O
is possible for this file.
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDeviceObject;
PFAST_IO_DISPATCH fastIoDispatch;
BOOLEAN result;
PAGED_CODE();
if (DeviceObject->DeviceExtension) {
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Pass through logic for this type of Fast I/O
//
nextDeviceObject = ((PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION) DeviceObject->DeviceExtension)->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject;
ASSERT(nextDeviceObject);
fastIoDispatch = nextDeviceObject->DriverObject->FastIoDispatch;
if (VALID_FAST_IO_DISPATCH_HANDLER( fastIoDispatch, FastIoQueryOpen )) {
PIO_STACK_LOCATION irpSp = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation( Irp );
//
// Before calling the next filter, we must make sure their device
// object is in the current stack entry for the given IRP
//
irpSp->DeviceObject = nextDeviceObject;
result = (fastIoDispatch->FastIoQueryOpen)(
Irp,
NetworkInformation,
nextDeviceObject );
//
// Always restore the IRP back to our device object
//
irpSp->DeviceObject = DeviceObject;
return result;
}
}
return FALSE;
}
#if WINVER >= 0x0501 /* See comment in DriverEntry */
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// FSFilter callback handling routines
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
SfPreFsFilterPassThrough (
IN PFS_FILTER_CALLBACK_DATA Data,
OUT PVOID *CompletionContext
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the FS Filter pre-operation "pass through" routine.
Arguments:
Data - The FS_FILTER_CALLBACK_DATA structure containing the information
about this operation.
CompletionContext - A context set by this operation that will be passed
to the corresponding SfPostFsFilterOperation call.
Return Value:
Returns STATUS_SUCCESS if the operation can continue or an appropriate
error code if the operation should fail.
--*/
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( Data );
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( CompletionContext );
ASSERT( IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( Data->DeviceObject ) );
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
VOID
SfPostFsFilterPassThrough (
IN PFS_FILTER_CALLBACK_DATA Data,
IN NTSTATUS OperationStatus,
IN PVOID CompletionContext
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine is the FS Filter post-operation "pass through" routine.
Arguments:
Data - The FS_FILTER_CALLBACK_DATA structure containing the information
about this operation.
OperationStatus - The status of this operation.
CompletionContext - A context that was set in the pre-operation
callback by this driver.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( Data );
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( OperationStatus );
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( CompletionContext );
ASSERT( IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( Data->DeviceObject ) );
}
#endif
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Support routines
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
SfAttachDeviceToDeviceStack (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT SourceDevice,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT TargetDevice,
IN OUT PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedToDeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine attaches the SourceDevice to the TargetDevice's stack and
returns the device object SourceDevice was directly attached to in
AttachedToDeviceObject. Note that the SourceDevice does not necessarily
get attached directly to TargetDevice. The SourceDevice will get attached
to the top of the stack of which TargetDevice is a member.
VERSION NOTE:
In Windows XP, a new API was introduced to close a rare timing window that
can cause IOs to start being sent to a device before its
AttachedToDeviceObject is set in its device extension. This is possible
if a filter is attaching to a device stack while the system is actively
processing IOs. The new API closes this timing window by setting the
device extension field that holds the AttachedToDeviceObject while holding
the IO Manager's lock that protects the device stack.
A sufficient work around for earlier versions of the OS is to set the
AttachedToDeviceObject to the device object that the SourceDevice is most
likely to attach to. While it is possible that another filter will attach
in between the SourceDevice and TargetDevice, this will prevent the
system from bug checking if the SourceDevice receives IOs before the
AttachedToDeviceObject is correctly set.
For a driver built in the Windows 2000 build environment, we will always
use the work-around code to attach. For a driver that is built in the
Windows XP or later build environments (therefore you are building a
multiversion driver), we will determine which method of attachment to use
based on which APIs are available.
Arguments:
SourceDevice - The device object to be attached to the stack.
TargetDevice - The device that we currently think is the top of the stack
to which SourceDevice should be attached.
AttachedToDeviceObject - This is set to the device object to which
SourceDevice is attached if the attach is successful.
Return Value:
Return STATUS_SUCCESS if the device is successfully attached. If
TargetDevice represents a stack to which devices can no longer be attached,
STATUS_NO_SUCH_DEVICE is returned.
--*/
{
PAGED_CODE();
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
if (IS_WINDOWSXP_OR_LATER()) {
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.AttachDeviceToDeviceStackSafe );
return (gSfDynamicFunctions.AttachDeviceToDeviceStackSafe)( SourceDevice,
TargetDevice,
AttachedToDeviceObject );
} else {
ASSERT( NULL == gSfDynamicFunctions.AttachDeviceToDeviceStackSafe );
#endif
*AttachedToDeviceObject = TargetDevice;
*AttachedToDeviceObject = IoAttachDeviceToDeviceStack( SourceDevice,
TargetDevice );
if (*AttachedToDeviceObject == NULL) {
return STATUS_NO_SUCH_DEVICE;
}
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
}
#endif
}
NTSTATUS
SfAttachToFileSystemDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PNAME_CONTROL DeviceName
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This will attach to the given file system device object. We attach to
these devices so we will know when new volumes are mounted.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The File System CDO to attach to
Name - An already initialized name control used to retrieve names.
This is passed in to reduce the number of strings buffers on
the stack.
Return Value:
Status of the operation
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT newDeviceObject;
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt;
UNICODE_STRING fsrecName;
NTSTATUS status;
PNAME_CONTROL fsName;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// See if this is a file system type we care about. If not, return.
//
if (!IS_DESIRED_DEVICE_TYPE(DeviceObject->DeviceType)) {
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
//
// See if we should attach to the standard file system recognizer device
// or not
//
if (!FlagOn(SfDebug, SFDEBUG_ATTACH_TO_FSRECOGNIZER)) {
//
// See if this is one of the standard Microsoft file system recognizer
// devices (see if this device is in the FS_REC driver). If so skip
// it. We no longer attach to file system recognizer devices, we
// simply wait for the real file system driver to load.
//
RtlInitUnicodeString( &fsrecName, L"\\FileSystem\\Fs_Rec" );
fsName = NLGetAndAllocateObjectName( DeviceObject->DriverObject,
&gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
if (fsName == NULL) {
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfAttachToFileSystemDevice: Error retrieving name, may attach to FS recognizer, status=%08x\n",
STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES) );
} else if (RtlCompareUnicodeString( &fsName->Name,
&fsrecName, TRUE ) == 0) {
//
// If it is a recognizer, don't attach
//
NLFreeNameControl( fsName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
NLFreeNameControl( fsName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
}
//
// We want to attach to this file system. Create a new device object we
// can attach with.
//
status = IoCreateDevice( gSFilterDriverObject,
sizeof( SFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION ),
NULL,
DeviceObject->DeviceType,
0,
FALSE,
&newDeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
return status;
}
//
// Propagate flags from Device Object we are trying to attach to.
// Note that we do this before the actual attachment to make sure
// the flags are properly set once we are attached (since an IRP
// can come in immediately after attachment but before the flags would
// be set).
//
if ( FlagOn( DeviceObject->Flags, DO_BUFFERED_IO )) {
SetFlag( newDeviceObject->Flags, DO_BUFFERED_IO );
}
if ( FlagOn( DeviceObject->Flags, DO_DIRECT_IO )) {
SetFlag( newDeviceObject->Flags, DO_DIRECT_IO );
}
if ( FlagOn( DeviceObject->Characteristics, FILE_DEVICE_SECURE_OPEN ) ) {
SetFlag( newDeviceObject->Characteristics, FILE_DEVICE_SECURE_OPEN );
}
//
// Initialize the device extension.
//
devExt = newDeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
devExt->Flags = 0;
NLInitDeviceExtensionHeader( &devExt->NLExtHeader,
newDeviceObject,
NULL );
//
// Set the name. We allocate from non-paged pool so this memory is always
// available for debugging (never gets paged out).
//
status = NLAllocateAndCopyUnicodeString( &devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
&DeviceName->Name,
SFLT_POOL_TAG_DEVNAME );
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
goto ErrorCleanupDevice;
}
//
// Do the attachment.
//
status = SfAttachDeviceToDeviceStack( newDeviceObject,
DeviceObject,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto ErrorCleanupDevice;
}
//
// Mark we are done initializing
//
ClearFlag( newDeviceObject->Flags, DO_DEVICE_INITIALIZING );
//
// Display who we have attached to
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfAttachToFileSystemDevice: Attaching %p to file system %p \"%wZ\" (%s)\n",
newDeviceObject,
DeviceObject,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
GET_DEVICE_TYPE_NAME(newDeviceObject->DeviceType)) );
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// In Windows XP, the IO Manager provided APIs to safely enumerate all the
// device objects for a given driver. This allows filters to attach to
// all mounted volumes for a given file system at some time after the
// volume has been mounted. There is no support for this functionality
// in Windows 2000.
//
// MULTIVERSION NOTE:
//
// If built for Windows XP or later, this driver is built to run on
// multiple versions. When this is the case, we will test
// for the presence of the new IO Manager routines that allow for volume
// enumeration. If they are not present, we will not enumerate the volumes
// when we attach to a new file system.
//
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
if (IS_WINDOWSXP_OR_LATER()) {
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList &&
NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDiskDeviceObject &&
NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef &&
NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetLowerDeviceObject );
//
// Enumerate all the mounted devices that currently
// exist for this file system and attach to them.
//
status = SfEnumerateFileSystemVolumes( DeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
IoDetachDevice( devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject );
goto ErrorCleanupDevice;
}
}
#endif
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Cleanup error handling
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
ErrorCleanupDevice:
SfCleanupMountedDevice( newDeviceObject );
IoDeleteDevice( newDeviceObject );
return status;
}
VOID
SfDetachFromFileSystemDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
Given a base file system device object, this will scan up the attachment
chain looking for our attached device object. If found it will detach
us from the chain.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The file system device to detach from.
Return Value:
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT ourAttachedDevice;
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Skip the base file system device object (since it can't be us)
//
ourAttachedDevice = DeviceObject->AttachedDevice;
while (NULL != ourAttachedDevice) {
if (IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( ourAttachedDevice )) {
devExt = ourAttachedDevice->DeviceExtension;
//
// Display who we detached from
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfDetachFromFileSystemDevice: Detaching %p from file system %p \"%wZ\" (%s)\n",
ourAttachedDevice,
devExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
&devExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
GET_DEVICE_TYPE_NAME(ourAttachedDevice->DeviceType)) );
//
// Detach us from the object just below us
// Cleanup and delete the object
//
SfCleanupMountedDevice( ourAttachedDevice );
IoDetachDevice( DeviceObject );
IoDeleteDevice( ourAttachedDevice );
return;
}
//
// Look at the next device up in the attachment chain
//
DeviceObject = ourAttachedDevice;
ourAttachedDevice = ourAttachedDevice->AttachedDevice;
}
}
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
NTSTATUS
SfEnumerateFileSystemVolumes (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT FSDeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
Enumerate all the mounted devices that currently exist for the given file
system and attach to them. We do this because this filter could be loaded
at any time and there might already be mounted volumes for this file system.
Arguments:
FSDeviceObject - The device object for the file system we want to enumerate
Return Value:
The status of the operation
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT newDeviceObject;
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION newDevExt;
PDEVICE_OBJECT *devList;
PDEVICE_OBJECT storageStackDeviceObject;
PNAME_CONTROL devName;
NTSTATUS status;
ULONG numDevices;
ULONG i;
BOOLEAN isShadowCopyVolume;
BOOLEAN hasLock = FALSE;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Find out how big of an array we need to allocate for the
// mounted device list.
//
status = (gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList)(
FSDeviceObject->DriverObject,
NULL,
0,
&numDevices);
//
// We only need to get this list of there are devices. If we
// don't get an error there are no devices so go on.
//
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
return status;
}
ASSERT(STATUS_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL == status);
//
// Allocate memory for the list of known devices
//
numDevices += 8; //grab a few extra slots
devList = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( NonPagedPool,
(numDevices * sizeof(PDEVICE_OBJECT)),
SFLT_POOL_TAG_ENUMFSVOL );
if (NULL == devList) {
return STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
//
// Now get the list of devices. If we get an error again
// something is wrong, so just fail.
//
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList );
status = (gSfDynamicFunctions.EnumerateDeviceObjectList)(
FSDeviceObject->DriverObject,
devList,
(numDevices * sizeof(PDEVICE_OBJECT)),
&numDevices);
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
ExFreePoolWithTag( devList, SFLT_POOL_TAG_ENUMFSVOL );
return status;
}
//
// Allocate the name control structure. We'll use this same name
// buffer each time through the for loop.
//
status = NLAllocateNameControl( &devName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// If we couldn't get it then we can not process any of the
// entries, release all of the device objects and return.
//
for (i=0; i<numDevices; i++) {
ObDereferenceObject( devList[i] );
}
ExFreePoolWithTag( devList, SFLT_POOL_TAG_ENUMFSVOL );
goto SkipAttach;
}
//
// Walk the given list of devices and attach to them if we should.
//
for (i=0; i < numDevices; i++) {
//
// Initialize state so it will look like a clean name each time
//
devName->Name.Length = 0;
storageStackDeviceObject = NULL;
newDeviceObject = NULL;
try {
//
// Do not attach if:
// - This is the control device object (the one passed in)
// - The device type does not match
// - We are already attached to it.
//
if ((devList[i] == FSDeviceObject) ||
(devList[i]->DeviceType != FSDeviceObject->DeviceType) ||
SfIsAttachedToDevice( devList[i], NULL )) {
leave;
}
//
// See if this device has a name. If so, then it must
// be a control device so don't attach to it. This handles
// drivers with more then one control device (like FastFat).
// We also don't want to attach if we could not get a name.
//
status = SfGetBaseDeviceObjectName( devList[i], devName );
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status) || (devName->Name.Length > 0)) {
leave;
}
//
// Get the real (disk/storage stack) device object associated
// with this file system device object. Only try to attach
// if we have a disk/storage stack device object.
//
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDiskDeviceObject );
status = (gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDiskDeviceObject)( devList[i],
&storageStackDeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
storageStackDeviceObject = NULL;
leave;
}
//
// Determine if this is a shadow copy volume. If so don't
// attach to it.
// NOTE: There is no reason sfilter shouldn't attach to these
// volumes, this is simply a sample of how to not
// attach if you don't want to
//
status = SfIsShadowCopyVolume ( storageStackDeviceObject,
&isShadowCopyVolume );
if (NT_SUCCESS(status) &&
isShadowCopyVolume &&
!FlagOn(SfDebug,SFDEBUG_ATTACH_TO_SHADOW_COPIES)) {
PNAME_CONTROL shadowDeviceName;
//
// Get the name for the debug display
//
shadowDeviceName = NLGetAndAllocateObjectName( storageStackDeviceObject,
&gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfEnumerateFileSystemVolumes Not attaching to Volume %p \"%wZ\", shadow copy volume\n",
storageStackDeviceObject,
shadowDeviceName ? &shadowDeviceName->Name :
&gInsufficientResourcesUnicode) );
if (shadowDeviceName != NULL) {
NLFreeNameControl( shadowDeviceName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
}
leave;
}
//
// Allocate a new device object to attach with
//
status = IoCreateDevice( gSFilterDriverObject,
sizeof( SFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION ),
NULL,
devList[i]->DeviceType,
0,
FALSE,
&newDeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
newDeviceObject = NULL;
leave;
}
//
// Initialize the device extension.
//
newDevExt = newDeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
newDevExt->Flags = 0;
NLInitDeviceExtensionHeader( &newDevExt->NLExtHeader,
newDeviceObject,
storageStackDeviceObject );
//
// Set storage stack device name. Just reuse the name
// NAME_CONTROL.
//
devName->Name.Length = 0;
status = NLGetObjectName( storageStackDeviceObject,
devName );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status)) {
leave;
}
//
// Copy it to the device extension. We allocate from non-paged
// pool so this memory is always available for debugging (never
// gets paged out).
//
status = NLAllocateAndCopyUnicodeString( &newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName,
&devName->Name,
SFLT_POOL_TAG_DEVNAME );
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
leave;
}
//
// We have done a lot of work since the last time
// we tested to see if we were already attached
// to this device object. Test again, this time
// with a lock, and attach if we are not attached.
// The lock is used to atomically test if we are
// attached, and then do the attach.
//
ExAcquireFastMutex( &gSfilterAttachLock );
hasLock = TRUE;
//
// See if we are already attached, if so don't attach again
//
if (SfIsAttachedToDevice( devList[i], NULL )) {
leave;
}
//
// Attach to volume.
//
status = SfAttachToMountedDevice( devList[i],
newDeviceObject );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// The attachment failed, cleanup. Note that
// we continue processing so we will cleanup
// the reference counts and try to attach to
// the rest of the volumes.
//
// One of the reasons this could have failed
// is because this volume is just being
// mounted as we are attaching and the
// DO_DEVICE_INITIALIZING flag has not yet
// been cleared. A filter could handle
// this situation by pausing for a short
// period of time and retrying the attachment a
// limited number of times.
//
leave;
}
//
// Release the lock.
//
ExReleaseFastMutex( &gSfilterAttachLock );
hasLock = FALSE;
//
// We just successfully attached, get the DOS device name
// (if the appropriate debug flags are set). Need to do this
// after the mutex is released because SfGetDosName does I/O.
//
if (FlagOn( SfDebug, SFDEBUG_GET_DOS_NAMES )) {
NLGetDosDeviceName( newDeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader );
}
//
// Mark not to free the device object
//
newDeviceObject = NULL;
} finally {
if (hasLock) {
ExReleaseFastMutex( &gSfilterAttachLock );
}
//
// Remove reference added by IoGetDiskDeviceObject.
// We only need to hold this reference until we are
// successfully attached to the current volume. Once
// we are successfully attached to devList[i], the
// IO Manager will make sure that the underlying
// storageStackDeviceObject will not go away until
// the file system stack is torn down.
//
if (storageStackDeviceObject != NULL) {
ObDereferenceObject( storageStackDeviceObject );
}
//
// Cleanup the device object if still defined
//
if (newDeviceObject != NULL) {
SfCleanupMountedDevice( newDeviceObject );
IoDeleteDevice( newDeviceObject );
}
//
// Dereference the object (reference added by
// IoEnumerateDeviceObjectList)
//
ObDereferenceObject( devList[i] );
}
}
NLFreeNameControl( devName, &gSfNameBufferLookasideList );
SkipAttach:
//
// We are going to ignore any errors received while attaching. We
// simply won't be attached to those volumes if we get an error
//
status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
//
// Free the memory we allocated for the list.
//
ExFreePoolWithTag( devList, SFLT_POOL_TAG_ENUMFSVOL );
return status;
}
#endif
NTSTATUS
SfAttachToMountedDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT SFilterDeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This will attach to a DeviceObject that represents a mounted volume.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The device to attach to
SFilterDeviceObject - Our device object we are going to attach
Return Value:
Status of the operation
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION newDevExt = SFilterDeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
NTSTATUS status;
ULONG i;
PAGED_CODE();
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( SFilterDeviceObject ));
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
ASSERT(!SfIsAttachedToDevice ( DeviceObject, NULL ));
#endif
//
// Propagate flags from Device Object we are trying to attach to.
// Note that we do this before the actual attachment to make sure
// the flags are properly set once we are attached (since an IRP
// can come in immediately after attachment but before the flags would
// be set).
//
if (FlagOn( DeviceObject->Flags, DO_BUFFERED_IO )) {
SetFlag( SFilterDeviceObject->Flags, DO_BUFFERED_IO );
}
if (FlagOn( DeviceObject->Flags, DO_DIRECT_IO )) {
SetFlag( SFilterDeviceObject->Flags, DO_DIRECT_IO );
}
ASSERT(newDevExt->NLExtHeader.ThisDeviceObject == SFilterDeviceObject);
//
// It is possible for this attachment request to fail because this device
// object has not finished initializing. This can occur if this filter
// loaded just as this volume was being mounted.
//
for (i=0; i < 8; i++) {
LARGE_INTEGER interval;
//
// Attach our device object to the given device object
// The only reason this can fail is if someone is trying to dismount
// this volume while we are attaching to it.
//
status = SfAttachDeviceToDeviceStack( SFilterDeviceObject,
DeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject );
if (NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
//
// Finished all initialization of the new device object, so clear
// the initializing flag now. This allows other filters to now
// attach to our device object.
//
ClearFlag( SFilterDeviceObject->Flags, DO_DEVICE_INITIALIZING );
//
// Display the name
//
SF_LOG_PRINT( SFDEBUG_DISPLAY_ATTACHMENT_NAMES,
("SFilter!SfAttachToMountedDevice: Attaching %p to volume %p \"%wZ\"\n",
SFilterDeviceObject,
newDevExt->NLExtHeader.AttachedToDeviceObject,
&newDevExt->NLExtHeader.DeviceName) );
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
//
// Delay, giving the device object a chance to finish its
// initialization so we can try again
//
interval.QuadPart = (500 * DELAY_ONE_MILLISECOND);
KeDelayExecutionThread( KernelMode, FALSE, &interval );
}
return status;
}
VOID
SfCleanupMountedDevice (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This cleans up any necessary data in the device extension to prepare for
this memory to be freed.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The device we are cleaning up
Return Value:
None
--*/
{
PSFILTER_DEVICE_EXTENSION devExt = DeviceObject->DeviceExtension;
ASSERT(IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( DeviceObject ));
//
// Free any memory allocated for the DeviceName and/or DosName.
//
NLCleanupDeviceExtensionHeader( &devExt->NLExtHeader );
}
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// These helper routines are only needed when enumerating all volumes in the
// system, which is only supported on Windows XP and later.
//
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
NTSTATUS
SfGetBaseDeviceObjectName (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
OUT PNAME_CONTROL Name
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This locates the base device object in the given attachment chain and then
returns the name of that object.
Arguments:
Object - The object whose name we want
Name - Pointer to a user-allocated name control which gets the device
object name.
Return Value:
None
--*/
{
NTSTATUS status;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Get the base file system device object
//
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef );
DeviceObject = (gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef)( DeviceObject );
//
// Get the name of that object
//
status = NLGetObjectName( DeviceObject, Name );
//
// Remove the reference added by IoGetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef
//
ObDereferenceObject( DeviceObject );
return status;
}
#endif
//
// VERSION NOTE:
//
// In Windows 2000, the APIs to safely walk an arbitrary file system device
// stack were not supported. If we can guarantee that a device stack won't
// be torn down during the walking of the device stack, we can walk from
// the base file system's device object up to the top of the device stack
// to see if we are attached. We know the device stack will not go away if
// we are in the process of processing a mount request OR we have a file object
// open on this device.
//
// In Windows XP and later, the IO Manager provides APIs that will allow us to
// walk through the chain safely using reference counts to protect the device
// object from going away while we are inspecting it. This can be done at any
// time.
//
// MULTIVERSION NOTE:
//
// If built for Windows XP or later, this driver is built to run on
// multiple versions. When this is the case, we will test for the presence of
// the new IO Manager routines that allow for a filter to safely walk the file
// system device stack and use those APIs if they are present to determine if
// we have already attached to this volume. If these new IO Manager routines
// are not present, we will assume that we are at the bottom of the file
// system stack and walk up the stack looking for our device object.
//
BOOLEAN
SfIsAttachedToDevice (
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedDeviceObject OPTIONAL
)
{
PAGED_CODE();
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
if (IS_WINDOWSXP_OR_LATER()) {
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetLowerDeviceObject &&
NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetDeviceAttachmentBaseRef );
return SfIsAttachedToDeviceWXPAndLater( DeviceObject, AttachedDeviceObject );
} else {
#endif
return SfIsAttachedToDeviceW2K( DeviceObject, AttachedDeviceObject );
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
}
#endif
}
BOOLEAN
SfIsAttachedToDeviceW2K (
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedDeviceObject OPTIONAL
)
/*++
Routine Description:
VERSION: Windows 2000
This routine walks up the device stack from the DeviceObject passed in
looking for a device object that belongs to our filter.
Note: If AttachedDeviceObject is returned with a non-NULL value,
there is a reference on the AttachedDeviceObject that must
be cleared by the caller.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The device chain we want to look through
AttachedDeviceObject - Set to the deviceObject which FileSpy
has previously attached to DeviceObject.
Return Value:
TRUE if we are attached, FALSE if not
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT currentDevice;
PAGED_CODE();
for (currentDevice = DeviceObject;
currentDevice != NULL;
currentDevice = currentDevice->AttachedDevice) {
if (IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( currentDevice )) {
//
// We are attached. If requested, return the found device object.
//
if (ARGUMENT_PRESENT(AttachedDeviceObject)) {
ObReferenceObject( currentDevice );
*AttachedDeviceObject = currentDevice;
}
return TRUE;
}
}
//
// We did not find ourselves on the attachment chain. Return a NULL
// device object pointer (if requested) and return we did not find
// ourselves.
//
if (ARGUMENT_PRESENT(AttachedDeviceObject)) {
*AttachedDeviceObject = NULL;
}
return FALSE;
}
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
BOOLEAN
SfIsAttachedToDeviceWXPAndLater (
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
PDEVICE_OBJECT *AttachedDeviceObject OPTIONAL
)
/*++
Routine Description:
VERSION: Windows XP and later
This walks down the attachment chain looking for a device object that
belongs to this driver. If one is found, the attached device object
is returned in AttachedDeviceObject.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The device chain we want to look through
AttachedDeviceObject - The Sfilter device attached to this device.
Return Value:
TRUE if we are attached, FALSE if not
--*/
{
PDEVICE_OBJECT currentDevObj;
PDEVICE_OBJECT nextDevObj;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Get the device object at the TOP of the attachment chain
//
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetAttachedDeviceReference );
currentDevObj = (gSfDynamicFunctions.GetAttachedDeviceReference)( DeviceObject );
//
// Scan down the list to find our device object.
//
do {
if (IS_MY_DEVICE_OBJECT( currentDevObj )) {
//
// We have found that we are already attached. If we are
// returning the device object, leave it referenced else remove
// the reference.
//
if (ARGUMENT_PRESENT(AttachedDeviceObject)) {
*AttachedDeviceObject = currentDevObj;
} else {
ObDereferenceObject( currentDevObj );
}
return TRUE;
}
//
// Get the next attached object. This puts a reference on
// the device object.
//
ASSERT( NULL != gSfDynamicFunctions.GetLowerDeviceObject );
nextDevObj = (gSfDynamicFunctions.GetLowerDeviceObject)( currentDevObj );
//
// Dereference our current device object, before
// moving to the next one.
//
ObDereferenceObject( currentDevObj );
currentDevObj = nextDevObj;
} while (NULL != currentDevObj);
//
// We did not find ourselves on the attachment chain. Return a NULL
// device object pointer (if requested) and return we did not find
// ourselves.
//
if (ARGUMENT_PRESENT(AttachedDeviceObject)) {
*AttachedDeviceObject = NULL;
}
return FALSE;
}
#endif
VOID
SfReadDriverParameters (
IN PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine tries to read the sfilter-specific parameters from
the registry. These values will be found in the registry location
indicated by the RegistryPath passed in.
Arguments:
RegistryPath - the path key passed to the driver during driver entry.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
OBJECT_ATTRIBUTES attributes;
HANDLE driverRegKey;
NTSTATUS status;
ULONG resultLength;
UNICODE_STRING valueName;
UCHAR buffer[sizeof( KEY_VALUE_PARTIAL_INFORMATION ) + sizeof( LONG )];
PAGED_CODE();
//
// If this value is not the default value then somebody has already
// explicitly set it so don't override those settings.
//
if (0 == SfDebug) {
//
// Open the desired registry key
//
InitializeObjectAttributes( &attributes,
RegistryPath,
OBJ_CASE_INSENSITIVE,
NULL,
NULL );
status = ZwOpenKey( &driverRegKey,
KEY_READ,
&attributes );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
return;
}
//
// Read the DebugDisplay value from the registry.
//
RtlInitUnicodeString( &valueName, L"DebugFlags" );
status = ZwQueryValueKey( driverRegKey,
&valueName,
KeyValuePartialInformation,
buffer,
sizeof(buffer),
&resultLength );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
SfDebug = *((PLONG) &
(((PKEY_VALUE_PARTIAL_INFORMATION) buffer)->Data));
}
//
// Close the registry entry
//
ZwClose(driverRegKey);
}
}
NTSTATUS
SfIsShadowCopyVolume (
IN PDEVICE_OBJECT StorageStackDeviceObject,
OUT PBOOLEAN IsShadowCopy
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine will determine if the given volume is for a ShadowCopy volume
or some other type of volume.
VERSION NOTE:
ShadowCopy volumes were introduced in Windows XP, therefore, if this
driver is running on W2K, we know that this is not a shadow copy volume.
Also note that in Windows XP, we need to test to see if the driver name
of this device object is \Driver\VolSnap in addition to seeing if this
device is read-only. For Windows Server 2003, we can infer that
this is a ShadowCopy by looking for a DeviceType == FILE_DEVICE_VIRTUAL_DISK
and read-only volume.
Arguments:
StorageStackDeviceObject - pointer to the disk device object
IsShadowCopy - returns TRUE if this is a shadow copy, FALSE otherwise
Return Value:
The status of the operation. If this operation fails IsShadowCopy is
always set to FALSE.
--*/
{
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Default to NOT a shadow copy volume
//
*IsShadowCopy = FALSE;
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
if (IS_WINDOWS2000()) {
#endif
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( StorageStackDeviceObject );
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
#if WINVER >= 0x0501
}
if (IS_WINDOWSXP()) {
UNICODE_STRING volSnapDriverName;
WCHAR buffer[MAX_DEVNAME_LENGTH];
PUNICODE_STRING storageDriverName;
ULONG returnedLength;
NTSTATUS status;
//
// In Windows XP, all ShadowCopy devices were of type FILE_DISK_DEVICE.
// If this does not have a device type of FILE_DISK_DEVICE, then
// it is not a ShadowCopy volume. Return now.
//
if (FILE_DEVICE_DISK != StorageStackDeviceObject->DeviceType) {
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
//
// Unfortunately, looking for the FILE_DEVICE_DISK isn't enough. We
// need to find out if the name of this driver is \Driver\VolSnap as
// well.
//
storageDriverName = (PUNICODE_STRING) buffer;
RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString( storageDriverName,
Add2Ptr( storageDriverName,
sizeof( UNICODE_STRING ) ),
sizeof( buffer ) - sizeof( UNICODE_STRING ) );
status = ObQueryNameString( StorageStackDeviceObject,
(POBJECT_NAME_INFORMATION)storageDriverName,
storageDriverName->MaximumLength,
&returnedLength );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
return status;
}
RtlInitUnicodeString( &volSnapDriverName, L"\\Driver\\VolSnap" );
if (RtlEqualUnicodeString( storageDriverName,
&volSnapDriverName, TRUE )) {
//
// This is a ShadowCopy volume, so set our return parameter to true.
//
*IsShadowCopy = TRUE;
} else {
//
// This is not a ShadowCopy volume, but IsShadowCopy is already
// set to FALSE. Fall through to return to the caller.
//
NOTHING;
}
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
} else {
PIRP irp;
KEVENT event;
IO_STATUS_BLOCK iosb;
NTSTATUS status;
//
// For Windows Server 2003 and later, it is sufficient to test for a
// device type of FILE_DEVICE_VIRTUAL_DISK and that the device
// is read-only to identify a ShadowCopy.
//
//
// If this does not have a device type of FILE_DEVICE_VIRTUAL_DISK,
// then it is not a ShadowCopy volume. Return now.
//
if (FILE_DEVICE_VIRTUAL_DISK != StorageStackDeviceObject->DeviceType) {
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
//
// It has the correct device type, see if it is marked as read only.
//
// NOTE: You need to be careful which device types you do this
// operation on. It is accurate for this type but for other
// device types it may return misleading information. For
// example the current Microsoft CD-ROM driver always returns
// CD media as readonly, even if the media may be writable.
// On other types this state may change.
//
KeInitializeEvent( &event, NotificationEvent, FALSE );
irp = IoBuildDeviceIoControlRequest( IOCTL_DISK_IS_WRITABLE,
StorageStackDeviceObject,
NULL,
0,
NULL,
0,
FALSE,
&event,
&iosb );
//
// If we could not allocate an IRP, return an error
//
if (irp == NULL) {
return STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
//
// Call the storage stack and see if this is readonly
//
status = IoCallDriver( StorageStackDeviceObject, irp );
if (status == STATUS_PENDING) {
(VOID)KeWaitForSingleObject( &event,
Executive,
KernelMode,
FALSE,
NULL );
status = iosb.Status;
}
//
// If the media is write protected then this is a shadow copy volume
//
if (STATUS_MEDIA_WRITE_PROTECTED == status) {
*IsShadowCopy = TRUE;
status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
//
// Return the status of the IOCTL. IsShadowCopy is already set to
// FALSE which is what we want if STATUS_SUCCESS was returned or if
// an error was returned.
//
return status;
}
#endif
}
/*++
Copyright (c) 1989-1999 Microsoft Corporation
Module Name:
namelookup.c
Abstract:
Header file which contains the definitions that may be
shared with the file spy kernel debugger extensions
Environment:
Kernel mode
--*/
//
// Fixes Win2K compatibility regarding lookaside lists.
//
#include "precomp.h"
#define NL_POOL_TAG 'tPuq'
#if WINVER == 0x0500
#define RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString(_ucStr,_buf,_bufSize) \
((_ucStr)->Buffer = (_buf), \
(_ucStr)->Length = 0, \
(_ucStr)->MaximumLength = (USHORT)(_bufSize))
#define ExFreePoolWithTag( a, b ) ExFreePool( (a) )
#ifndef min
#define min(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#endif
#ifndef max
#define max(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#endif
#endif
//
// The context used to send the task of getting the DOS device name off to
// a worker thread.
//
typedef struct _NL_DOS_NAME_COMPLETION_CONTEXT {
WORK_QUEUE_ITEM WorkItem;
//
// The DeviceObject whose name is being retrieved. We need this in addition
// to the other fields so we can make sure it doesn't disappear while
// we're retrieving the name.
//
PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject;
//
// The name library device extension header of the device object to get
// the DOS name of.
//
PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader;
} NL_DOS_NAME_COMPLETION_CONTEXT, *PNL_DOS_NAME_COMPLETION_CONTEXT;
//
// Function prototypes
//
NTSTATUS
NLPQueryFileSystemForFileName (
__in PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT NextDeviceObject,
__inout PNAME_CONTROL FileName
);
NTSTATUS
NLPQueryCompletion (
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
__in PIRP Irp,
__in PKEVENT SynchronizingEvent
);
VOID
NLPGetDosDeviceNameWorker (
__in PNL_DOS_NAME_COMPLETION_CONTEXT Context
);
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLPQueryFileSystemForFileName)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLInitNameControl)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLCleanupNameControl)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLGetAndAllocateObjectName)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLGetObjectName)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLGetDosDeviceName)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLPGetDosDeviceNameWorker)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLAllocateAndCopyUnicodeString)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLInitNameControl)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLCleanupNameControl)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLReallocNameControl)
#pragma alloc_text(PAGE, NLCheckAndGrowNameControl)
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Name lookup functions.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
NLGetFullPathName (
__in PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
__inout PNAME_CONTROL FileNameControl,
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader,
__in NAME_LOOKUP_FLAGS LookupFlags,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList,
__out PBOOLEAN CacheName
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine retrieves the full pathname of the FileObject. Note that
the buffers containing pathname components may be stored in paged pool,
therefore if we are at DISPATCH_LEVEL we cannot look up the name.
The file is looked up one of the following ways based on the LookupFlags:
1. FlagOn( FileObject->Flags, FO_VOLUME_OPEN ) or
(FileObject->FileName.Length == 0). This is a volume open, so just use
DeviceName from the NLExtHeader for the FileName, if it exists.
2. NAMELOOKUPFL_IN_CREATE and NAMELOOKUPFL_OPEN_BY_ID are set.
This is an open by file id, so format the file id into the FileName
string if there is enough room.
3. NAMELOOKUPFL_IN_CREATE set and FileObject->RelatedFileObject != NULL.
This is a relative open, therefore the fullpath file name must
be built up from the name of the FileObject->RelatedFileObject
and FileObject->FileName.
4. NAMELOOKUPFL_IN_CREATE and FileObject->RelatedFileObject == NULL.
This is an absolute open, therefore the fullpath file name is
found in FileObject->FileName.
5. No LookupFlags set.
This is a lookup sometime after CREATE. FileObject->FileName is
no longer guaranteed to be valid, so we call
NLPQueryFileSystemForFileName which rolls a IRP_MJ_QUERY_INFORMATION to
get the file name.
NONPAGED: This routine is called by FILESPY in the paging file path so it
must be non-paged.
Arguments:
FileObject - Pointer to the FileObject to the get name of.
FileNameControl - A caller-allocated name control that will be filled with
the filename. The string will be NULL terminated.
NLExtHeader - The portion of a device extension needed to build the file
name.
LookupFlags - Flags that determine how the name is generated.
CacheName - TRUE if the returned name should be saved in the cache, FALSE
if the returned name should NOT be saved in the cache.
Return Value:
STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES if there was not enough memory to retrieve
the full name. If this is the case, FileNameControl->Name.Length will
be set to 0. Do not expect any specific value for CacheName.
STATUS_BUFFER_OVERFLOW if the status buffer to hold the file ID or object ID
was not large enough. If this is the case, FileNameControl->Name.Length
will be set to 0. Do not expect any specific value for CacheName.
STATUS_SUCCESS if
1) The full name was retrieved successfully, OR
2) At DPC level, full name could not be retrieved, OR
3) The name was only to be looked up in the cache, OR
4) Nested operation, full name could not be retrieved, OR
--*/
{
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
NTSTATUS returnValue = STATUS_SUCCESS;
ULONG i;
BOOLEAN cacheName = TRUE;
LONG count;
//
// Copy over the name the user gave for this device. These names
// should be meaningful to the user. Note that we do not do this for
// NETWORK file system because internally they already show the
// connection name. If this is a direct device open of the network
// file system device, we will copy over the device name to be
// returned to the user.
//
if (FILE_DEVICE_NETWORK_FILE_SYSTEM != NLExtHeader->ThisDeviceObject->DeviceType &&
FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_USE_DOS_DEVICE_NAME ) &&
NLExtHeader->DosName.Length != 0) {
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
NLExtHeader->DosName.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlCopyUnicodeString( &FileNameControl->Name, &NLExtHeader->DosName );
} else if (FlagOn( FileObject->Flags, FO_DIRECT_DEVICE_OPEN )) {
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
NLExtHeader->DeviceName.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlCopyUnicodeString( &FileNameControl->Name,
&NLExtHeader->DeviceName );
//
// We are now done since there will be no more to the name in this
// case, so return TRUE.
//
*CacheName = TRUE;
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
} else {
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
NLExtHeader->DeviceName.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlCopyUnicodeString( &FileNameControl->Name,
&NLExtHeader->DeviceName );
}
//
// See if we can request the name
//
if (FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_ONLY_CHECK_CACHE )) {
# define NotInCacheMsg L"[-=Not In Cache=-]"
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
sizeof( NotInCacheMsg ) );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
NotInCacheMsg );
*CacheName = TRUE;
return STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
}
//
// Can not get the name at DPC level
//
if (KeGetCurrentIrql() > APC_LEVEL) {
# define AtDPCMsg L"[-=At DPC Level=-]"
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
sizeof( AtDPCMsg ) );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
AtDPCMsg );
*CacheName = FALSE;
return STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
}
//
// If there is a ToplevelIrp then this is a nested operation and
// there might be other locks held. Can not get name without the
// potential of deadlocking.
//
if (IoGetTopLevelIrp() != NULL) {
# define NestedMsg L"[-=Nested Operation=-]"
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
sizeof( NestedMsg ) );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
NestedMsg );
*CacheName = FALSE;
return STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
}
//
// CASE 1: This FileObject refers to a Volume open. Either the
// flag is set or no filename is specified.
//
if (FlagOn( FileObject->Flags, FO_VOLUME_OPEN ) ||
(FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_IN_CREATE ) &&
(FileObject->FileName.Length == 0) &&
(FileObject->RelatedFileObject == NULL))) {
//
// We've already copied the VolumeName so just return.
//
}
//
// CASE 2: We are opening the file by ID.
//
else if (FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_IN_CREATE ) &&
FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_OPEN_BY_ID )) {
# define OBJECT_ID_KEY_LENGTH 16
# define ID_BUFFER_SIZE 40
//
// Static buffer big enough for a file Id or object Id.
//
WCHAR idName[ID_BUFFER_SIZE];
if (FileObject->FileName.Length == sizeof(LONGLONG)) {
//
// Opening by FILE ID, generate a name.
//
// To get the actual file name, you could use the file id to open
// the file and then get the file name.
//
count = _snwprintf( idName,
sizeof(idName),
L"<%016I64x>",
*((PLONGLONG)FileObject->FileName.Buffer) );
//
// If the buffer wasn't big enough for the entire string, fail.
//
if (count < 0) {
FileNameControl->Name.Length = 0;
return STATUS_BUFFER_OVERFLOW;
}
} else if ((FileObject->FileName.Length == OBJECT_ID_KEY_LENGTH) ||
(FileObject->FileName.Length == OBJECT_ID_KEY_LENGTH +
sizeof(WCHAR)))
{
PUCHAR idBuffer;
//
// Opening by Object ID, generate a name
//
// To get the actual file name, you could use the file id to open
// the file and then get the file name.
//
idBuffer = (PUCHAR)&FileObject->FileName.Buffer[0];
if (FileObject->FileName.Length != OBJECT_ID_KEY_LENGTH) {
//
// Skip win32 backslash at start of buffer
//
idBuffer = (PUCHAR)&FileObject->FileName.Buffer[1];
}
count = _snwprintf( idName,
sizeof(idName),
L"<%08x-%04hx-%04hx-%04hx-%04hx%08x>",
*(PULONG)&idBuffer[0],
*(PUSHORT)&idBuffer[0+4],
*(PUSHORT)&idBuffer[0+4+2],
*(PUSHORT)&idBuffer[0+4+2+2],
*(PUSHORT)&idBuffer[0+4+2+2+2],
*(PULONG)&idBuffer[0+4+2+2+2+2] );
//
// If the buffer wasn't big enough for the entire string, fail.
//
if (count < 0) {
FileNameControl->Name.Length = 0;
return STATUS_BUFFER_OVERFLOW;
}
} else {
//
// Unknown ID format.
//
count = _snwprintf( idName,
sizeof(idName),
L"[-=Unknown ID (Len=%u)=-]\n",
FileObject->FileName.Length );
}
//
// Append the idName to FileNameControl.
//
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
ID_BUFFER_SIZE );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
idName );
//
// Don't cache the ID name
//
cacheName = FALSE;
//
// Continue on to the end of the routine and return STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL
// since we are not able to return a "usable" file name (caller cannot
// use the file name we return in other calls because it is not
// "valid").
//
returnValue = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
}
//
// CASE 3: We are opening a file that has a RelatedFileObject.
//
else if (FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_IN_CREATE ) &&
(NULL != FileObject->RelatedFileObject)) {
//
// Must be a relative open. We cannot use ObQueryNameString to get
// the name of the RelatedFileObject because it may result in
// deadlock.
//
PNAME_CONTROL relativeName;
//ULONG returnLength;
status = NLAllocateNameControl( &relativeName, LookasideList );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
status = NLPQueryFileSystemForFileName( FileObject->RelatedFileObject,
NLExtHeader->AttachedToDeviceObject,
relativeName );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status ))
{
//
// We were able to get the relative FileoBject's name.
// Build up the file name in the following format:
// [volumeName]\[relativeFileObjectName]\[FileObjectName]
// The VolumeName is already in FileNameControl if we've got one.
//
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
relativeName->Name.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeStringToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
&relativeName->Name );
} else {
//
// The query for the relative FileObject name was
// unsuccessful. Build up the file name in the following format:
// [volumeName]\...\[FileObjectName]
// The volumeName is already in FileNameControl if we've got one.
# define RFOPlaceholder L"...\\"
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
sizeof( RFOPlaceholder ) );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
RFOPlaceholder );
cacheName = FALSE;
}
//
// If there is not a slash and the end of the related file object
// string and there is not a slash at the front of the file object
// string, then add one.
//
if (((FileNameControl->Name.Length < sizeof(WCHAR) ||
(FileNameControl->Name.Buffer[(FileNameControl->Name.Length/sizeof(WCHAR))-1] != L'\\')))
&& ((FileObject->FileName.Length < sizeof(WCHAR)) ||
(FileObject->FileName.Buffer[0] != L'\\')))
{
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
sizeof(WCHAR) );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeToString( &FileNameControl->Name, L"\\" );
}
NLFreeNameControl( relativeName, LookasideList );
//
// At this time, copy over the FileObject->FileName to FileNameControl.
//
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
FileObject->FileName.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeStringToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
&FileObject->FileName );
//
// Continue on to the end of the routine and return
// STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL since we are not able to return a "usable"
// file name (caller cannot use the file name we return in other
// calls because it is not "valid").
//
returnValue = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
}
//
// CASE 4: We have a open on a file with an absolute path.
//
else if (FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_IN_CREATE ) &&
(FileObject->RelatedFileObject == NULL) ) {
//
// We have an absolute path, so try to copy that into FileNameControl.
//
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
FileObject->FileName.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeStringToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
&FileObject->FileName );
}
//
// CASE 5: We are retrieving the file name sometime after the
// CREATE operation.
//
else if (!FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_IN_CREATE )) {
PNAME_CONTROL nameInfo;
//ULONG returnLength;
status = NLAllocateNameControl( &nameInfo, LookasideList );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
status = NLPQueryFileSystemForFileName( FileObject,
NLExtHeader->AttachedToDeviceObject,
nameInfo );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
nameInfo->Name.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeStringToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
&nameInfo->Name );
} else {
//
// Got an error trying to get the file name from the base file
// system, so fail.
//
count = _snwprintf( nameInfo->Name.Buffer,
nameInfo->BufferSize,
L"[-=Error 0x%x Getting Name=-]",
status );
nameInfo->Name.Length = (USHORT)max( 0, count );
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileNameControl,
FileNameControl->Name.Length +
nameInfo->Name.Length );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
goto NoResources;
}
RtlAppendUnicodeStringToString( &FileNameControl->Name,
&nameInfo->Name );
cacheName = FALSE;
return STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
}
NLFreeNameControl( nameInfo, LookasideList );
}
//
// When we get here we have a valid name.
// Sometimes when we query a name it has a trailing slash, other times
// it doesn't. To make sure the contexts are correct we are going to
// remove a trailing slash if there is not a ":" just before it.
//
if ((FileNameControl->Name.Length >= (2*sizeof(WCHAR))) &&
(FileNameControl->Name.Buffer[(FileNameControl->Name.Length/sizeof(WCHAR))-1] == L'\\') &&
(FileNameControl->Name.Buffer[(FileNameControl->Name.Length/sizeof(WCHAR))-2] != L':'))
{
FileNameControl->Name.Length -= sizeof(WCHAR);
}
//
// See if we are actually opening the target directory. If so then
// remove the trailing name and slash. Note that we won't remove
// the initial slash (just after the colon).
//
if (FlagOn( LookupFlags, NLFL_OPEN_TARGET_DIR ) &&
(FileNameControl->Name.Length > 0))
{
i = (FileNameControl->Name.Length / sizeof(WCHAR)) - 1;
//
// See if the path ends in a backslash, if so skip over it
// (since the file system did).
//
if ((i > 0) &&
(FileNameControl->Name.Buffer[i] == L'\\') &&
(FileNameControl->Name.Buffer[i-1] != L':')) {
i--;
}
//
// Scan backwards over the last component
//
for ( ; i > 0; i-- ) {
if (FileNameControl->Name.Buffer[i] == L'\\') {
if ((i > 0) && (FileNameControl->Name.Buffer[i-1] == L':')) {
i++;
}
FileNameControl->Name.Length = (USHORT)(i * sizeof(WCHAR));
break;
}
}
}
*CacheName = cacheName;
return returnValue;
NoResources:
*CacheName = FALSE;
FileNameControl->Name.Length = 0;
return status;
}
NTSTATUS
NLPQueryFileSystemForFileName (
__in PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT NextDeviceObject,
__inout PNAME_CONTROL FileName
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine rolls an IRP to query the name of the
FileObject parameter from the base file system.
Note: ObQueryNameString CANNOT be used here because it
would cause recursive lookup of the file name for FileObject.
Arguments:
FileObject - the file object for which we want the name.
NextDeviceObject - the device object for the next driver in the
stack. This is where we want to start our request
for the name of FileObject.
FileName - Receives the name. This must be memory that safe to write
to from kernel space.
Return Value:
Returns the status of the operation.
--*/
{
PIRP irp;
PIO_STACK_LOCATION irpSp;
KEVENT event;
IO_STATUS_BLOCK ioStatus;
NTSTATUS status;
PFILE_NAME_INFORMATION nameInfo = NULL;
ULONG nameInfoLength;
PAGED_CODE();
__try {
//
// We'll start with a small buffer and grow it if needed.
//
nameInfoLength = 256;
nameInfo = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( PagedPool,
nameInfoLength,
NL_POOL_TAG );
if (nameInfo == NULL) {
status = STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
__leave;
}
//
// Try getting the name. If the IRP fails, then our buffer is too small.
// We'll grow it and try again (hence the loop). We can get the needed
// buffer size from the FileNameLength field of FILE_NAME_INFORMATION.
//
while (TRUE) {
irp = IoAllocateIrp( NextDeviceObject->StackSize, FALSE );
if (irp == NULL) {
status = STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
__leave;
}
//
// Set our current thread as the thread for this
// IRP so that the IO Manager always knows which
// thread to return to if it needs to get back into
// the context of the thread that originated this
// IRP.
//
irp->Tail.Overlay.Thread = PsGetCurrentThread();
//
// Set that this IRP originated from the kernel so that
// the IOManager knows that the buffers do not
// need to be probed.
//
irp->RequestorMode = KernelMode;
//
// Initialize the UserIosb and UserEvent in the
//
ioStatus.Status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
ioStatus.Information = 0;
irp->UserIosb = &ioStatus;
irp->UserEvent = NULL; //already zeroed
//
// Set the IRP_SYNCHRONOUS_API to denote that this
// is a synchronous IO request.
//
irp->Flags = IRP_SYNCHRONOUS_API;
irpSp = IoGetNextIrpStackLocation( irp );
irpSp->MajorFunction = IRP_MJ_QUERY_INFORMATION;
irpSp->FileObject = FileObject;
//
// Setup the parameters for IRP_MJ_QUERY_INFORMATION.
// The buffer we want to be filled in should be placed in
// the system buffer.
//
irp->AssociatedIrp.SystemBuffer = nameInfo;
irpSp->Parameters.QueryFile.Length = nameInfoLength;
irpSp->Parameters.QueryFile.FileInformationClass = FileNameInformation;
//
// Set up the completion routine so that we know when our
// request for the file name is completed. At that time,
// we can free the IRP.
//
KeInitializeEvent( &event, NotificationEvent, FALSE );
IoSetCompletionRoutine( irp,
NLPQueryCompletion,
&event,
TRUE,
TRUE,
TRUE );
status = IoCallDriver( NextDeviceObject, irp );
if (STATUS_PENDING == status) {
(VOID) KeWaitForSingleObject( &event,
Executive,
KernelMode,
FALSE,
NULL );
}
//
// Verify that our completion routine has been called.
//
ASSERT(KeReadStateEvent(&event) ||
!NT_SUCCESS(ioStatus.Status));
//
// If the IRP succeeded, go ahead and copy the name and return.
//
if (NT_SUCCESS( ioStatus.Status )) {
//
// We retrieved a valid name, set into buffer
// Make sure the buffer is big enough to hold the given name
//
status = NLCheckAndGrowNameControl( FileName,
(USHORT)nameInfo->FileNameLength );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// Copy the name from nameInfo buffer into name control
//
RtlCopyMemory( FileName->Name.Buffer,
nameInfo->FileName,
nameInfo->FileNameLength );
FileName->Name.Length = (USHORT)nameInfo->FileNameLength;
}
__leave;
} else if (ioStatus.Status == STATUS_BUFFER_OVERFLOW) {
//
// Buffer was too small, so grow it and try again. We need space
// in the buffer for the name and the FileNameLength ULONG.
//
nameInfoLength = (USHORT)nameInfo->FileNameLength +
sizeof( ULONG );
ExFreePoolWithTag( nameInfo, NL_POOL_TAG );
nameInfo = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( PagedPool,
nameInfoLength,
NL_POOL_TAG );
if (nameInfo == NULL) {
status = STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
__leave;
}
} else {
//
// The query name failed, we are done
//
status = ioStatus.Status;
__leave;
}
}
} __finally {
if (nameInfo != NULL) {
ExFreePoolWithTag( nameInfo, NL_POOL_TAG );
}
}
return status;
}
NTSTATUS
NLPQueryCompletion (
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
__in PIRP Irp,
__in PKEVENT SynchronizingEvent
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine does the cleanup necessary once the query request completed
by the file system.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - This will be NULL since we originated this
IRP.
Irp - The IO request structure containing the information
about the current state of our file name query.
SynchronizingEvent - The event to signal to notify the
originator of this request that the operation is
complete.
Return Value:
Returns STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED so that IO Manager
will not try to free the IRP again.
--*/
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER( DeviceObject );
//
// Make sure that the IRP status is copied over to the users
// IO_STATUS_BLOCK so that the originator of this IRP will know
// the final status of this operation.
//
ASSERT( NULL != Irp->UserIosb );
*Irp->UserIosb = Irp->IoStatus;
//
// Signal SynchronizingEvent so that the originator of this
// IRP know that the operation is completed.
//
KeSetEvent( SynchronizingEvent, IO_NO_INCREMENT, FALSE );
//
// We are now done, so clean up the IRP that we allocated.
//
IoFreeIrp( Irp );
//
// If we return STATUS_SUCCESS here, the IO Manager will
// perform the cleanup work that it thinks needs to be done
// for this IO operation. This cleanup work includes:
// * Copying data from the system buffer to the users buffer
// if this was a buffered IO operation.
// * Freeing any MDLs that are in the IRP.
// * Copying the Irp->IoStatus to Irp->UserIosb so that the
// originator of this IRP can see the final status of the
// operation.
// * If this was an asynchronous request or this was a
// synchronous request that got pending somewhere along the
// way, the IO Manager will signal the Irp->UserEvent, if one
// exists, otherwise it will signal the FileObject->Event.
// (This can have REALLY bad implications if the IRP originator
// did not an Irp->UserEvent and the IRP originator is not
// waiting on the FileObject->Event. It would not be that
// farfetched to believe that someone else in the system is
// waiting on FileObject->Event and who knows who will be
// awoken as a result of the IO Manager signaling this event.
//
// Since some of these operations require the originating thread's
// context (e.g., the IO Manager need the UserBuffer address to
// be valid when copy is done), the IO Manager queues this work
// to an APC on the IRPs originating thread.
//
// We can do this cleanup work more efficiently than the IO Manager
// since we are handling a very specific case. Therefore, it is better
// for us to perform the cleanup work here then free the IRP than passing
// control back to the IO Manager to do this work.
//
// By returning STATUS_MORE_PROCESS_REQUIRED, we tell the IO Manager
// to stop processing this IRP until it is told to restart processing
// with a call to IoCompleteRequest. Since the IO Manager has
// already performed all the work we want it to do on this
// IRP, we do the cleanup work, return STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED,
// and ask the IO Manager to resume processing by calling
// IoCompleteRequest.
//
return STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED;
}
PNAME_CONTROL
NLGetAndAllocateObjectName (
__in PVOID Object,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList
)
/*++
Routine description:
This routine will allocate the name control and retrieve the name of
the device object or driver object. If we can not get either a NULL
entry is returned.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The object to get the name for
ObjectName - The lookaside list to allocate from
Return Value:
Returns: NAME_CONTROL if we got the name. The caller must free the
name control when they are done.
Else NULL if no name could be retrieved.
--*/
{
NTSTATUS status;
PNAME_CONTROL objName;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Allocate name control
//
status = NLAllocateNameControl( &objName, LookasideList );
if (NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// Retrieve the name. Note that we don't test for an error because
// we want to use whatever name is returned.
//
status = NLGetObjectName( Object, objName );
} else {
//
// On a failure NLAllocateNameControl returns the buffer NULL'd,
// verify this
//
ASSERT(objName == NULL);
}
return objName;
}
NTSTATUS
NLGetObjectName (
__in PVOID Object,
__inout PNAME_CONTROL ObjectName
)
/*++
Routine description:
This routine reads the name from Object and copies it into the
given name control structure. The memory for ObjectName's buffer should
be allocated by the caller. We can use ObQueryNameString here because
Object is a device object or a driver object.
Arguments:
Object - Supplies the object being queried
ObjectName - The name control structure to store Object's name. Will
grow if needed to hold the object name.
Return Value:
Returns STATUS_SUCCESS if the name could be retrieved and successfully
copied into ObjectName.
Returns STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES if memory cannot be allocated to
store the name.
--*/
{
NTSTATUS status;
POBJECT_NAME_INFORMATION nameInfo;
ULONG lengthReturned = 0;
PAGED_CODE();
ASSERT( ARGUMENT_PRESENT( ObjectName ) );
//
// We just use the buffer in the name control to hold the
// OBJECT_NAME_INFORMATION structure plus name buffer. That
// way we don't have to do a separate allocation.
//
nameInfo = (POBJECT_NAME_INFORMATION) ObjectName->Name.Buffer;
//
// Query the object manager to get the name
//
status = ObQueryNameString( Object,
nameInfo,
ObjectName->Name.MaximumLength,
&lengthReturned );
//
// If we get back a status saying the buffer is too small,
// we can try to reallocate a node with the number of bytes needed
//
if (status == STATUS_INFO_LENGTH_MISMATCH) {
status = NLReallocNameControl( ObjectName,
lengthReturned,
NULL );
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// If we cannot successfully reallocate a node, we are probably
// out of memory. In this case we will just set the string to NULL
// and return the error
//
ObjectName->Name.Length = 0;
return status;
}
nameInfo = (POBJECT_NAME_INFORMATION) ObjectName->Name.Buffer;
status = ObQueryNameString( Object,
nameInfo,
ObjectName->Name.MaximumLength,
&lengthReturned );
}
//
// At this point we should only be getting back errors other than
// buffer not large enough (that should have been handled above)
//
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
int count = _snwprintf( ObjectName->Name.Buffer,
ObjectName->Name.MaximumLength,
L"[-=Error 0x%x Getting Name=-]",
status );
//
// We should never really get a negative count back because
// Name Control structures allocate a buffer of size 254 or greater
// Our error status should never cause us to have string > 254...
//
ObjectName->Name.Length = (USHORT)max( 0, count );
return status;
}
//
// We got the name, so now just need to shuffle everything into place.
//
ObjectName->Name.Length = nameInfo->Name.Length;
RtlMoveMemory( ObjectName->Name.Buffer,
nameInfo->Name.Buffer,
ObjectName->Name.Length );
return status;
}
VOID
NLGetDosDeviceName (
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine gets the DOS device name of DeviceObject. It uses a worker
thread due to the threat of deadlock (see inline comments).
NOTE: This routine will allocate (on success) the DosName buffer in
NLExtHeader. Call NLCleanupDeviceExtensionHeader when you tear down
your device extension to make sure this is freed.
Arguments:
DeviceObject - The object to get the DOS device name of.
NLExtHeader - The name lookup extension header for DeviceObject.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
PNL_DOS_NAME_COMPLETION_CONTEXT completionContext;
PAGED_CODE();
//
// Mount manager could be on the call stack below us holding
// a lock. NLPGetDosDeviceNameWorker will eventually query the mount
// manager which will cause a deadlock in this scenario.
// So, we need to do this work in a worker thread.
//
completionContext = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( NonPagedPool,
sizeof( NL_DOS_NAME_COMPLETION_CONTEXT ),
NL_POOL_TAG );
if (completionContext == NULL) {
//
// If we cannot allocate our completion context, we will not
// get the DOS name.
//
NLExtHeader->DosName.Length = 0;
} else {
//
// Initialize a work item. CompletionContext keeps track
// of the work queue item and the data that we need
// to pass to NLPGetDosDeviceNameWorker in the worker thread.
//
ExInitializeWorkItem( &completionContext->WorkItem,
NLPGetDosDeviceNameWorker,
completionContext );
//
// Don't let the DeviceObject get deleted while we get the DOS
// device name asynchronously.
//
ObReferenceObject( DeviceObject );
//
// Setup the context.
//
completionContext->DeviceObject = DeviceObject;
completionContext->NLExtHeader = NLExtHeader;
//
// Queue the work item so that it will be run in a
// worker thread at some point.
//
ExQueueWorkItem( &completionContext->WorkItem ,
DelayedWorkQueue );
}
}
VOID
NLPGetDosDeviceNameWorker (
__in PNL_DOS_NAME_COMPLETION_CONTEXT Context
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine uses RtlVolumeDeviceToDosName to get the DOS device name of a
device object. Note that RtlVolumeDeviceToDosName is obsolete, but we use
it so the code is backwards compatible with Win2K. If the DOS name cannot
be retrieved, we set the Length parameter of DosName to 0
Arguments:
NLExtHeader - The name lookup extension header corresponding with the device
object to get the name of.
Return Value:
None
--*/
{
NTSTATUS status;
PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER nlExtHeader;
PAGED_CODE();
ASSERT( Context != NULL );
nlExtHeader = Context->NLExtHeader;
//
// Get DOS device name if we have a storage stack device
// object to ask for it. The reason we might not have a storage
// stack device is if this is a Remote File System.
//
if (nlExtHeader->StorageStackDeviceObject == NULL) {
ObDereferenceObject( Context->DeviceObject );
ExFreePoolWithTag( Context, NL_POOL_TAG );
//
// Set the DosName to the empty string
//
nlExtHeader->DosName.Length = 0;
return;
}
ASSERT( nlExtHeader->StorageStackDeviceObject != NULL );
//
// Get the DOS device name
//
status = RtlVolumeDeviceToDosName( nlExtHeader->StorageStackDeviceObject,
&nlExtHeader->DosName);
if (!NT_SUCCESS( status )) {
//
// We couldn't get the DOS device name. Set the string to empty
//
nlExtHeader->DosName.Length = 0;
}
ObDereferenceObject( Context->DeviceObject );
ExFreePoolWithTag( Context, NL_POOL_TAG );
return;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Name lookup device extension header functions.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
VOID
NLInitDeviceExtensionHeader (
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader,
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT ThisDeviceObject,
__in_opt PDEVICE_OBJECT StorageStackDeviceObject
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine initializes the fields of a NL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER. All
pointer fields are set to NULL, and unicode strings are initialized as
empty. Use NLCleanupDeviceExtensionHeader to clean up a
NL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER.
NLExtHeader must *not* be NULL.
Arguments:
NLExtHeader - The name lookup extension header to initialize.
ThisDeviceObject - Device Object that this device extension is attached to
Return Value:
Pointer to the allocated and initialized name control.
If allocation fails, this function returns NULL.
--*/
{
ASSERT(NLExtHeader != NULL);
NLExtHeader->AttachedToDeviceObject = NULL;
NLExtHeader->ThisDeviceObject = ThisDeviceObject;
NLExtHeader->StorageStackDeviceObject = StorageStackDeviceObject;
RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString( &NLExtHeader->DeviceName, NULL, 0 );
RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString( &NLExtHeader->DosName, NULL, 0 );
}
VOID
NLCleanupDeviceExtensionHeader (
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine frees any memory associated with the given name lookup
extension header. This may include the DosName unicode string and buffer,
and the DeviceName.
Arguments:
NLExtHeader - The name lookup extension header to clean up.
Return Value:
None
--*/
{
if (NLExtHeader->DosName.Buffer != NULL) {
ExFreePool( NLExtHeader->DosName.Buffer );
}
if (NLExtHeader->DeviceName.Buffer != NULL) {
ExFreePool( NLExtHeader->DeviceName.Buffer );
}
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// General support routines
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
NLAllocateAndCopyUnicodeString (
__inout PUNICODE_STRING DestName,
__in PUNICODE_STRING SrcName,
__in ULONG PoolTag
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine will allocate a buffer big enough to hold the unicode string
in SrcName, copy the name, and properly setup DestName
Arguments:
DestName - the unicode string we are copying too
SrcName - the unicode string we are copying from
Return Value:
STATUS_SUCCESS - if it worked
STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCE - if we could not allocate pool
--*/
{
USHORT bufSize;
PVOID buf;
PAGED_CODE();
ASSERT(DestName->Buffer == NULL);
bufSize = SrcName->Length;
if (bufSize > 0) {
buf = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( NonPagedPool,
bufSize,
PoolTag );
if (buf == NULL) {
RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString( DestName, NULL, bufSize );
return STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString( DestName, buf, bufSize );
RtlCopyUnicodeString( DestName, SrcName );
} else {
RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString( DestName, NULL, bufSize );
}
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Routines to support generic name control structures that allow us
// to get names of arbitrary size.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
NLAllocateNameControl (
__out PNAME_CONTROL *NameControl,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine allocates a name control from LookasideList, initializes it,
and returns a pointer to it. If allocation fails, NULL is returned.
Use NLFreeNameControl to free a name control received from this routine.
NONPAGED: FILESPY needs to call this on the paging file path.
Arguments:
LookasideList - The lookaside list to allocate the name control from.
Return Value:
Pointer to the allocated and initialized name control.
If allocation fails, this function returns NULL.
--*/
{
PNAME_CONTROL nameCtrl = NULL;
nameCtrl = ExAllocateFromPagedLookasideList( LookasideList );
if (nameCtrl == NULL) {
*NameControl = NULL;
return STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
NLInitNameControl( nameCtrl );
*NameControl = nameCtrl;
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
VOID
NLFreeNameControl (
__in PNAME_CONTROL NameControl,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine frees a name control received from NLAllocateNameControl. It
cleans up the name control, including any larger buffer allocations, and
then frees the name control back to LookasideList. If NameControl is NULL,
this function does nothing.
Arguments:
NameControl - The name control release.
LookasideList - The lookaside list that this name control was initially
allocated from.
Return Value:
None.
--*/
{
if (NameControl != NULL) {
NLCleanupNameControl( NameControl );
ExFreeToPagedLookasideList( LookasideList, NameControl );
}
}
NTSTATUS
NLCheckAndGrowNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl,
__in USHORT NewSize
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine will check the name control's current buffer capacity. If
it is less than NewSize, a new larger name buffer will be allocated and put
into the name control structure. If there is already an allocated buffer it
will be freed. It will also copy any name information from the old buffer
into the new buffer.
Arguments:
NameCtrl - The name control we need a bigger buffer for
NewSize - Size of the new buffer
Return Value:
Returns STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES if a larger buffer cannot be
allocated.
--*/
{
PAGED_CODE();
if (NewSize > (NameCtrl->BufferSize - sizeof(WCHAR))) {
return NLReallocNameControl( NameCtrl,
(NewSize + sizeof(WCHAR)),
NULL );
}
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
VOID
NLInitNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This will initialize the name control structure. Use NLCleanupNameControl
when you are done with it.
Use NLAllocateNameControl and NLFreeNameControl if you need to
allocate & initialize / cleanup & deallocate a name control in one step.
Arguments:
NameCtrl - The name control to initialize.
Return Value:
None
--*/
{
PAGED_CODE();
NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer = NULL;
NameCtrl->BufferSize = sizeof( NameCtrl->SmallBuffer );
RtlInitEmptyUnicodeString( &NameCtrl->Name,
(PWCHAR)NameCtrl->SmallBuffer,
(USHORT)NameCtrl->BufferSize );
}
VOID
NLCleanupNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This will cleanup the name control structure, freeing any buffers
that were allocated for the NameCtrl.
Use NLAllocateNameControl and NLFreeNameControl if you need to
allocate & initialize / cleanup & deallocate a name control in one step.
Arguments:
NameCtrl - The NAME_CONTROL structure to cleanup.
Return Value:
None
--*/
{
PAGED_CODE();
if (NULL != NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer) {
ExFreePoolWithTag( NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer, NL_POOL_TAG );
NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer = NULL;
}
}
NTSTATUS
NLReallocNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl,
__in ULONG NewSize,
__out_opt PWCHAR *RetOriginalBuffer
)
/*++
Routine Description:
This routine will allocate a new larger name buffer and put it into the
NameControl structure. If there is already an allocated buffer it will
be freed. It will also copy any name information from the old buffer
into the new buffer.
Arguments:
NameCtrl - the name control we need a bigger buffer for
NewSize - size of the new buffer
RetOrignalBuffer - if defined, receives the buffer that we were
going to free. if NULL was returned no buffer needed to be freed.
WARNING: if this parameter is defined and a non-null value is returned
then the caller MUST free this memory else the memory will be lost.
Return Value:
Returns STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES if a larger buffer cannot be
allocated.
--*/
{
PUCHAR newBuffer;
PAGED_CODE();
ASSERT( NewSize > NameCtrl->BufferSize);
//
// Flag no buffer to return yet
//
if (RetOriginalBuffer) {
*RetOriginalBuffer = NULL;
}
//
// Allocate the new buffer
//
newBuffer = ExAllocatePoolWithTag( PagedPool, NewSize, NL_POOL_TAG );
if (NULL == newBuffer) {
return STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
//
// Copy data from old buffer if there is any, including any stream
// name component.
//
if (NameCtrl->Name.Length > 0) {
ASSERT( NewSize > (USHORT)NameCtrl->Name.Length);
RtlCopyMemory( newBuffer,
NameCtrl->Name.Buffer,
NameCtrl->Name.Length );
}
//
// If we had an old buffer free it if the caller doesn't want
// it passed back to him. This is done because there are
// cases where the caller has a pointer into the old buffer so
// it can't be freed yet. The caller must free this memory.
//
if (NULL != NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer) {
if (RetOriginalBuffer) {
*RetOriginalBuffer = (PWCHAR)NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer;
} else {
ExFreePoolWithTag( NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer, NL_POOL_TAG );
}
}
//
// Set the new buffer into the name control
//
NameCtrl->AllocatedBuffer = newBuffer;
NameCtrl->BufferSize = NewSize;
NameCtrl->Name.Buffer = (PWCHAR)newBuffer;
NameCtrl->Name.MaximumLength = (USHORT)min( 0xfff0, NewSize );
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
头文件:
namelookup.h
/*++
Copyright (c) 2004 Microsoft Corporation
Module Name:
namelookup.h
Abstract:
Header file containing the name lookup device extension and name lookup
function prototypes.
Environment:
Kernel mode
--*/
#ifndef __NAMELOOKUP_H__
#define __NAMELOOKUP_H__
#include "namelookupdef.h"
//
// Give pointer alignment characteristics for the different processor types
//
#if defined(_X86_)
# define DECLSPEC_PTRALIGN __declspec(align(4))
#elif defined(_AMD64_)
# define DECLSPEC_PTRALIGN __declspec(align(8))
#elif defined(_IA64_)
# define DECLSPEC_PTRALIGN __declspec(align(8))
#else
# error "No target architecture defined"
#endif
//
// These structures are used to retrieve the name of objects. To prevent
// allocating memory every time we get a name, and to prevent having large
// string buffers on the stack, this structure contains a small
// buffer (which should handle 90+% of all names). If we do overflow this
// buffer we will allocate a buffer big enough for the name.
//
typedef struct _NAME_CONTROL {
//
// UNICODE_STRING whos buffer is either SmallBuffer or AllocatedBuffer
// if a larger buffer was needed.
//
UNICODE_STRING Name;
//
// AllocatedBuffer is used when we need a buffer larger than SmallBuffer.
//
PUCHAR AllocatedBuffer;
//
// The size of whatever buffer is currently being used (SmallBuffer or
// AllocatedBuffer) in bytes.
//
ULONG BufferSize;
//
// This is the buffer that we start out with. The thinking is that this
// should be large enough for most names.
//
DECLSPEC_PTRALIGN UCHAR SmallBuffer[254];
} NAME_CONTROL, *PNAME_CONTROL;
//
// NL_EXTENSION is the part of a device extension that is needed
// by the name lookup routines. All the non-namelookup data contained
// here should be needed by any filter. Simply use this as part of
// any filter's device extension.
//
typedef struct _NL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER {
//
// Device Object this device extension is attached to
//
PDEVICE_OBJECT ThisDeviceObject;
//
// Device object this filter is directly attached to
//
PDEVICE_OBJECT AttachedToDeviceObject;
//
// When attached to Volume Device Objects, the physical device object
// that represents that volume. NULL when attached to Control Device
// objects.
//
PDEVICE_OBJECT StorageStackDeviceObject;
//
// DOS representation of the device name.
//
UNICODE_STRING DosName;
//
// Name for this device. If attached to a Volume Device Object it is the
// name of the physical disk drive. If attached to a Control Device
// Object it is the name of the Control Device Object. This is in the
// "\Device\...\" format.
//
UNICODE_STRING DeviceName;
} NL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER, *PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Name lookup functions.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
NLGetFullPathName (
__in PFILE_OBJECT FileObject,
__inout PNAME_CONTROL FileNameControl,
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader,
__in NAME_LOOKUP_FLAGS LookupFlags,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList,
__out PBOOLEAN CacheName
);
PNAME_CONTROL
NLGetAndAllocateObjectName (
__in PVOID Object,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList
);
NTSTATUS
NLGetObjectName (
__in PVOID Object,
__inout PNAME_CONTROL ObjectNameCtrl
);
VOID
NLGetDosDeviceName (
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject,
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader
);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// General support routines
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
NLAllocateAndCopyUnicodeString (
__inout PUNICODE_STRING DestName,
__in PUNICODE_STRING SrcName,
__in ULONG PoolTag
);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Name lookup device extension header functions.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
VOID
NLInitDeviceExtensionHeader (
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader,
__in PDEVICE_OBJECT ThisDeviceObject,
__in_opt PDEVICE_OBJECT StorageStackDeviceObject
);
VOID
NLCleanupDeviceExtensionHeader(
__in PNL_DEVICE_EXTENSION_HEADER NLExtHeader
);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Routines to support generic name control structures that allow us
// to get names of arbitrary size.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
NTSTATUS
NLAllocateNameControl (
__out PNAME_CONTROL *NameControl,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList
);
VOID
NLFreeNameControl (
__in PNAME_CONTROL NameControl,
__in PPAGED_LOOKASIDE_LIST LookasideList
);
NTSTATUS
NLCheckAndGrowNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl,
__in USHORT NewSize
);
VOID
NLInitNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl
);
VOID
NLCleanupNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl
);
NTSTATUS
NLReallocNameControl (
__inout PNAME_CONTROL NameCtrl,
__in ULONG NewSize,
__out_opt PWCHAR *RetOriginalBuffer
);
#endif
namelookupdef.h
/*++
Copyright (c) 1989-1999 Microsoft Corporation
Module Name:
namelookupdef.h
Abstract:
Header file containing the name lookup definitions needed by both user
and kernel mode. No kernel-specific data types are used here.
Environment:
User and kernel.
--*/
#ifndef __NAMELOOKUPDEF_H__
#define __NAMELOOKUPDEF_H__
//
// This is set to the number of characters we want to allow the
// device extension to store for the name used to identify
// a device object.
//
#define DEVICE_NAME_SZ 256
//
// This is set to the number of characters we want to allow the
// device extension to use for storing user-provided names.
// This is only used for devices whos type is FILE_DEVICE_NETWORK_FILE_SYSTEM
// since we cannot get a DOS device name for them.
//
#define USER_NAMES_SZ 256
//
// These are flags passed to the name lookup routine to identify different
// ways the name of a file can be obtained
//
typedef enum _NAME_LOOKUP_FLAGS {
//
// If set, only check in the name cache for the file name.
//
NLFL_ONLY_CHECK_CACHE = 0x00000001,
//
// If set, don't lookup the name
//
NLFL_NO_LOOKUP = 0x00000002,
//
// if set, we are in the CREATE operation and the full path filename may
// need to be built up from the related FileObject.
//
NLFL_IN_CREATE = 0x00000004,
//
// if set and we are looking up the name in the file object, the file
// object does not actually contain a name but it contains a file/object
// ID.
//
NLFL_OPEN_BY_ID = 0x00000008,
//
// If set, the target directory is being opened
//
NLFL_OPEN_TARGET_DIR = 0x00000010,
//
// If set, use the DOS device name (DosName) instead of the NT device name.
//
NLFL_USE_DOS_DEVICE_NAME = 0x00000020
} NAME_LOOKUP_FLAGS;
#endif
precomp.h
#include <ntifs.h>
#include <ntdddisk.h>
#include <ntimage.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windef.h>
#include <ntstrsafe.h>
#include "namelookup.h"
#include "namelookupdef.h"
#pragma warning(disable:4995)
安装代码:
#include <windows.h>
#include <winsvc.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <winioctl.h>
#define DRIVER_NAME "SfilterDrv"
#define DRIVER_PATH ".\\SfilterDrv.sys"
#define IOCTL_BASE 0x800
#define MY_CTL_CODE(i) \
CTL_CODE(FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN, IOCTL_BASE+i, METHOD_BUFFERED, FILE_ANY_ACCESS)
#define IOCTL_HELLO MY_CTL_CODE(0)
HANDLE g_hHandle = NULL;
//装载NT驱动程序
BOOL LoadDriver(char* lpszDriverName,char* lpszDriverPath)
{
char szDriverImagePath[256] = {0};
//得到完整的驱动路径
GetFullPathName(lpszDriverPath, 256, szDriverImagePath, NULL);
BOOL bRet = FALSE;
SC_HANDLE hServiceMgr=NULL;//SCM管理器的句柄
SC_HANDLE hServiceDDK=NULL;//NT驱动程序的服务句柄
//打开服务控制管理器
hServiceMgr = OpenSCManager( NULL, NULL, SC_MANAGER_ALL_ACCESS );
if( hServiceMgr == NULL )
{
//OpenSCManager失败
printf( "OpenSCManager() Failed %d ! \n", GetLastError() );
bRet = FALSE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
else
{
////OpenSCManager成功
printf( "OpenSCManager() ok ! \n" );
}
//创建驱动所对应的服务
hServiceDDK = CreateService( hServiceMgr,
lpszDriverName, //驱动程序的在注册表中的名字
lpszDriverName, // 注册表驱动程序的 DisplayName 值
SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS, // 加载驱动程序的访问权限
SERVICE_KERNEL_DRIVER,// 表示加载的服务是驱动程序
SERVICE_SYSTEM_START, // 注册表驱动程序的 Start 值
SERVICE_ERROR_IGNORE, // 注册表驱动程序的 ErrorControl 值
szDriverImagePath, // 注册表驱动程序的 ImagePath 值
"FSFilter Activity Monitor", //GroupOrder HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\GroupOrderList
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL);
DWORD dwRtn;
//判断服务是否失败
if( hServiceDDK == NULL )
{
dwRtn = GetLastError();
if( dwRtn != ERROR_IO_PENDING && dwRtn != ERROR_SERVICE_EXISTS )
{
//由于其他原因创建服务失败
printf( "CrateService() Failed %d ! \n", dwRtn );
bRet = FALSE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
else
{
//服务创建失败,是由于服务已经创立过
printf( "CrateService() Failed Service is ERROR_IO_PENDING or ERROR_SERVICE_EXISTS! \n" );
}
// 驱动程序已经加载,只需要打开
hServiceDDK = OpenService( hServiceMgr, lpszDriverName, SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS );
if( hServiceDDK == NULL )
{
//如果打开服务也失败,则意味错误
dwRtn = GetLastError();
printf( "OpenService() Failed %d ! \n", dwRtn );
bRet = FALSE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
else
{
printf( "OpenService() ok ! \n" );
}
}
else
{
printf( "CrateService() ok ! \n" );
}
//开启此项服务
bRet= StartService( hServiceDDK, NULL, NULL );
if( !bRet )
{
DWORD dwRtn = GetLastError();
if( dwRtn != ERROR_IO_PENDING && dwRtn != ERROR_SERVICE_ALREADY_RUNNING )
{
printf( "StartService() Failed %d ! \n", dwRtn );
bRet = FALSE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
else
{
if( dwRtn == ERROR_IO_PENDING )
{
//设备被挂住
printf( "StartService() Failed ERROR_IO_PENDING ! \n");
bRet = FALSE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
else
{
//服务已经开启
printf( "StartService() Failed ERROR_SERVICE_ALREADY_RUNNING ! \n");
bRet = TRUE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
}
}
bRet = TRUE;
//离开前关闭句柄
BeforeLeave:
if(hServiceDDK)
{
CloseServiceHandle(hServiceDDK);
}
if(hServiceMgr)
{
CloseServiceHandle(hServiceMgr);
}
return bRet;
}
//卸载驱动程序
BOOL UnloadDriver( char * szSvrName )
{
BOOL bRet = FALSE;
SC_HANDLE hServiceMgr=NULL;//SCM管理器的句柄
SC_HANDLE hServiceDDK=NULL;//NT驱动程序的服务句柄
SERVICE_STATUS SvrSta;
//打开SCM管理器
hServiceMgr = OpenSCManager( NULL, NULL, SC_MANAGER_ALL_ACCESS );
if( hServiceMgr == NULL )
{
//带开SCM管理器失败
printf( "OpenSCManager() Failed %d ! \n", GetLastError() );
bRet = FALSE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
else
{
//带开SCM管理器失败成功
printf( "OpenSCManager() ok ! \n" );
}
//打开驱动所对应的服务
hServiceDDK = OpenService( hServiceMgr, szSvrName, SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS );
if( hServiceDDK == NULL )
{
//打开驱动所对应的服务失败
printf( "OpenService() Failed %d ! \n", GetLastError() );
bRet = FALSE;
goto BeforeLeave;
}
else
{
printf( "OpenService() ok ! \n" );
}
//停止驱动程序,如果停止失败,只有重新启动才能,再动态加载。
if( !ControlService( hServiceDDK, SERVICE_CONTROL_STOP , &SvrSta ) )
{
printf( "ControlService() Failed %d !\n", GetLastError() );
}
else
{
//打开驱动所对应的失败
printf( "ControlService() ok !\n" );
}
//动态卸载驱动程序。
if( !DeleteService( hServiceDDK ) )
{
//卸载失败
printf( "DeleteSrevice() Failed %d !\n", GetLastError() );
}
else
{
//卸载成功
printf( "DelServer:deleteSrevice() ok !\n" );
}
bRet = TRUE;
BeforeLeave:
//离开前关闭打开的句柄
if(hServiceDDK)
{
CloseServiceHandle(hServiceDDK);
}
if(hServiceMgr)
{
CloseServiceHandle(hServiceMgr);
}
return bRet;
}
void TestDriver()
{
//测试驱动程序
g_hHandle = CreateFile(
"\\\\.\\SFilterDrv",
GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE,
FILE_SHARE_READ | FILE_SHARE_WRITE | FILE_SHARE_DELETE,
NULL,
OPEN_EXISTING,
FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL | FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED,
NULL
);
if( g_hHandle != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE )
{
printf( "Create Device ok ! \n" );
}
else
{
printf( "Create Device failed %d ! \n", GetLastError() );
return;
}
// CHAR bufRead[1024]={0};
// CHAR bufWrite[1024]="Hello, world";
//
// DWORD dwRead = 0;
// DWORD dwWrite = 0;
//
// ReadFile(hDevice, bufRead, 1024, &dwRead, NULL);
// WriteFile(hDevice, bufWrite, strlen(bufWrite)+1, &dwWrite, NULL);
//
// CHAR bufInput[1024] ="Hello, world";
// CHAR bufOutput[1024] = {0};
// DWORD dwRet = 0;
//
// DeviceIoControl(hDevice, IOCTL_HELLO, bufInput, sizeof(bufInput), bufOutput, sizeof(bufOutput), &dwRet, NULL);
CloseHandle( g_hHandle );
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//加载驱动
BOOL bRet = LoadDriver(DRIVER_NAME,DRIVER_PATH);
if (!bRet)
{
printf("LoadNTDriver error\n");
return 0;
}
//加载成功
printf( "press any to create device!\n" );
getch();
TestDriver();
//这时候你可以通过注册表,或其他查看符号连接的软件验证。
printf( "press any to unload the driver!\n" );
getch();
//卸载驱动
UnloadDriver(DRIVER_NAME);
if (!bRet)
{
printf("UnloadNTDriver error\n");
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
Sfilter框架已经将绑定等处理好了,用户只需要进行的操作是对拿到的数据进行处理。